Figure 4.
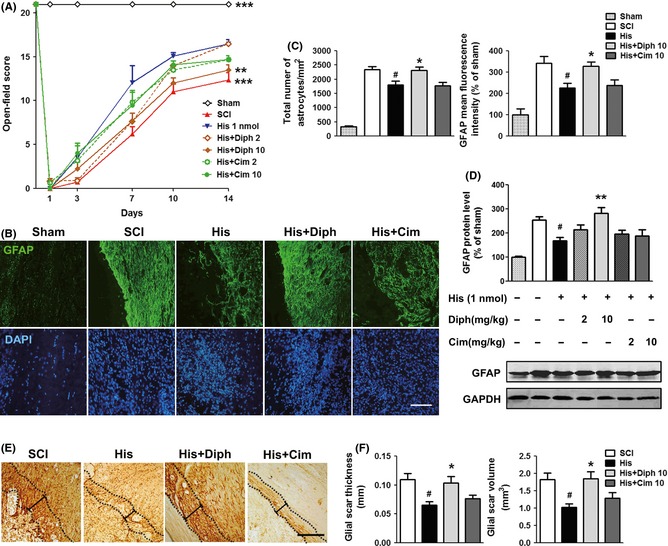
Inhibitory effect of histamine on reactive astrogliosis via stimulating histamine H1 receptor in SCI. (A) The BBB scores at 1, 3, 7, 10, and 14 dpo. n = 6. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 versus the histamine group. (B) Representative photographs from GFAP immunostaining of the lesion site at 14 dpo. (C) Quantitative assessments of the total number of astrocytes and GFAP fluorescence mean intensity. n = 4. # P < 0.05 versus SCI group, *P < 0.05 versus histamine group. (D) Western blot analysis of GFAP level in spinal cord. n = 3. # P < 0.05 versus SCI group, **P < 0.01 versus histamine group. (E) Representative photographs containing glial scar from DAB straining of GFAP. Scale bars: 200 μm. (F) Quantitative assessments of thickness and volume of glial scar. n = 4. # P < 0.05 versus SCI group, *P < 0.05 versus histamine group.
