Figure 1.
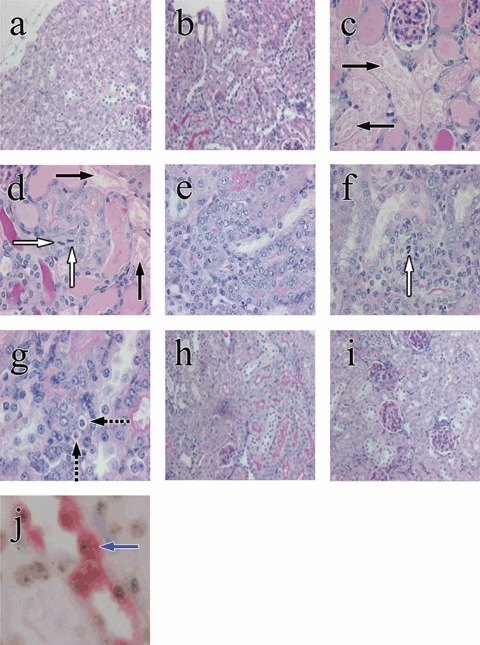
Examples of renal tubular histology in control and HgCl2‐treated mice, given or not given bone marrow cells (BMCs); periodic acid–Schiff stain (original magnifications). Renal tubular cells appeared normal in the control period (a, ×200) and in mice given BMCs throughout the experiment (b, ×200). Three days after HgCl2, renal tubular epithelial damage and tubular cell mitoses were seen in HgCl2‐treated mice given and not given BMCs (c and d, ×400). Black arrows indicate extensive renal tubular damage and necrosis (c, d) and white arrows indicate tubular epithelial mitosis (d). Seven days after HgCl2 damage, regenerative tubules with hypercellularity were seen in HgCl2‐treated mice given (e, ×400) or not given BMCs (f, ×400 and g, ×600). Dashed black arrows indicate apoptotic cells. Four weeks after HgCl2, most damaged tubules have regenerated in HgCl2‐treated mice given or not given BMCs (h and i, ×200). A blue arrow indicates A Y‐positive donor cell (brown dot) with megalin staining (red colour) (j, ×1000).
