FIG 5.
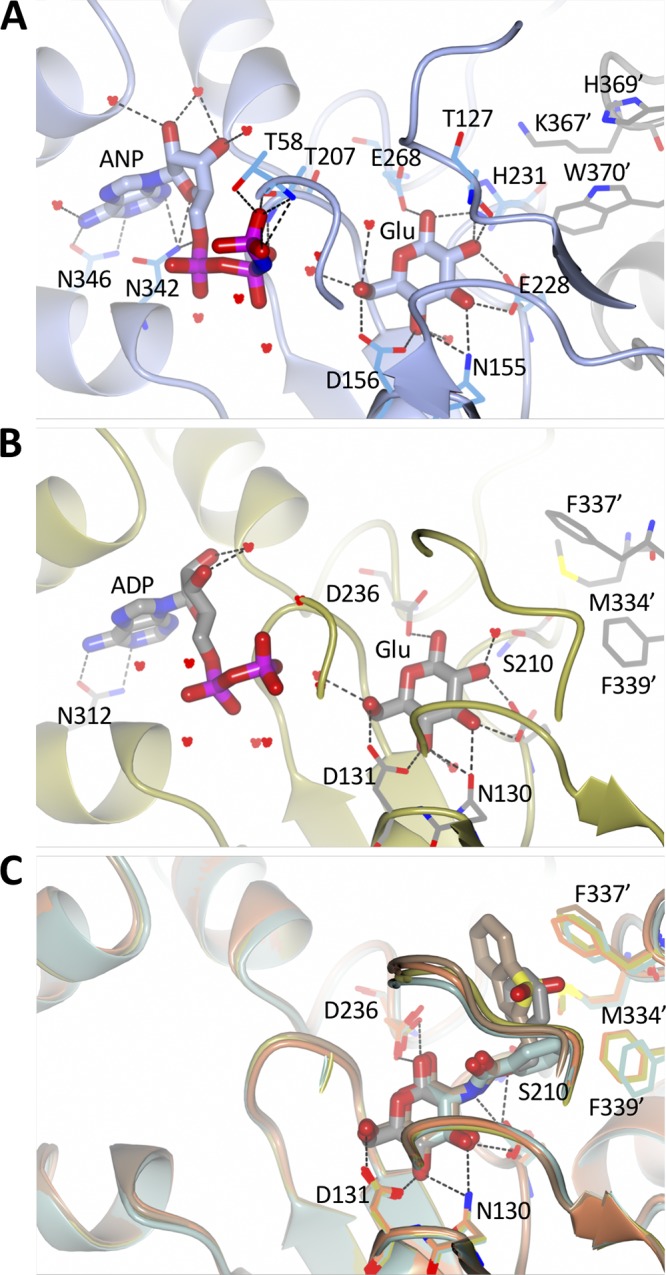
Nucleotide and glucose binding sites of various Glcks. (A) In NfGlck, AMPPNP (ANP) and glucose (Glu) are bound with a strong hydrogen bond network, including hydrogen bonds from the 1- and 2-hydroxyl groups to His231. AMPPNP and glucose are shown in sticks, while residues and water molecules interacting with the ligands are shown in thick bonds. Residues Lys367′, His369′, and Trp370 are from the other molecule in the crystallographic dimer. (B) In TcGlck, ADP and glucose are bound with a very similar hydrogen bond pattern. Ser210 replaces His231 and cannot engage in a hydrogen bond with glucose. Residues Met334′, Phe337′, and Phe339′ are located in the other chain of the dimer. (C) TcGlck bound to several glucosamine ligands (BENZ-GLCN, green, PDB entry 5BRD; CBZ-GLCN, gold, PDB entry 5BRE; HPOP-GLCN, orange, PDB entry 5BRF; BDT-GLCN, brown, PDB entry 5BRH), the amine moiety is part of the space that the His231 side chain of NfGlck occupies.
