Figure 2.
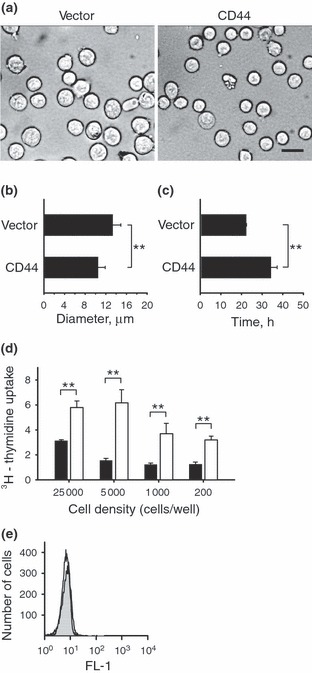
Impact of CD44 on cell size, doubling time, proliferation and apoptosis. (a–b) The sizes of E6.1 Jurkat cells expressing CD44 or transfected with the open vector control were evaluated under bright field microscopy. The E6.1 Jurkat cells expressing CD44 showed a modest but significant reduction in their diameters as compared with the open vector control cells (scale bar, 20 μm). (c) The doubling time of E6.1 Jurkat cells expressing CD44 was significantly increased as compared with the doubling time of open vector control E6.1 Jurkat cells. (d) The E6.1 Jurkat cells expressing CD44 (black bars) or the open vector control (white bars) were cultured at the indicated densities and pulsed with [3H]dT during the last 24 h of the culture period. Results show that reducing the number of cells did not restore the proliferation of CD44 expressing E6.1 Jurkat cells to the same level as the open vector control cells. These results suggest that CD44 did not impair proliferation due to contact inhibition. (e) Apoptosis of open vector control E6.1 Jurkat cells (open histogram) and CD44 expressing E6.1 Jurkat cells (closed histogram) were ascertained using Annexin V staining and FACS. We failed to detect CD44‐induced apoptosis as compared with the open vector control cells. Results show representative FACS histograms from triplicate experiments with similar results. Values in this figure are expressed as mean ± SD from 280 independently measured cells (b) or triplicate samples (c and d). Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (**P < 0.01).
