Figure 5.
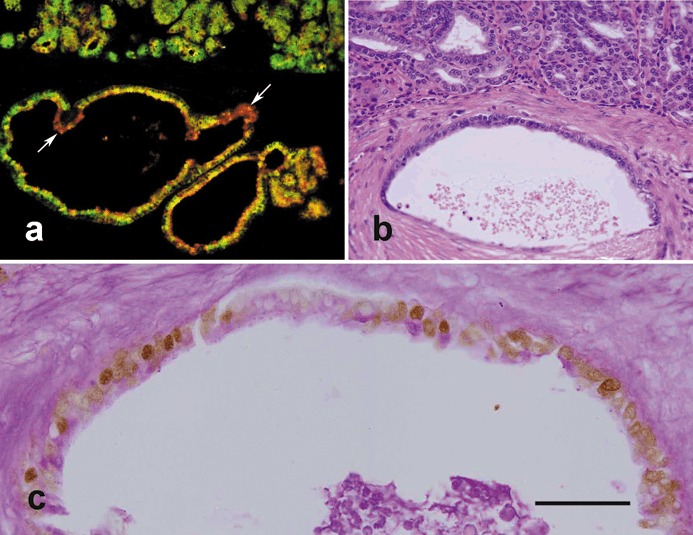
Analysis of invasive cells in the pyloric antral mucosae of 12‐month‐old TFF1 knockout mice. (a) Tissue was probed with both UEA‐I (red) and GSII (green) lectins and shows numerous double labelled cells (yellow) suggesting that uncommitted progenitors with dual features of pre‐pit and pre‐gland mucous cells are amplified and have invaded the muscularis mucosa to form variable profiles, mainly cyst‐like, in the submucosa. Note that a few cells appear mostly green and some appear mostly red (arrows) indicating the capacity of invading progenitors to differentiate. (b) A further pyloric antral mucosal tissue section stained with haematoxylin and eosin shows the basal portion of the antral mucosa with numerous small epithelial cells forming variable profiles, some of them having invaded the underlying submucosa to form a relatively large cyst‐like structure seen in the lower half of the figure. (c) Tissue section adjacent to (b), probed with anti‐proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) antibody and counterstained with periodic acid Schiff (PAS) as in Figure 3. Note nuclei of many of the invading cells lining the cyst‐like structure appear brownish and hence, PCNA‐positive. However, apical cytoplasm of the lining cells contains little or no mucus (PAS‐negative). Bar = 90 (a, b); 35 (c) µm.
