Figure 10.
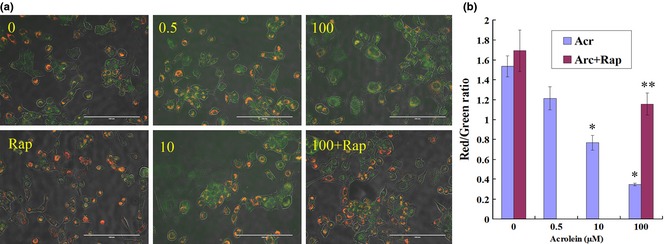
Rapamycin ( Rap ) alleviated acrolein ( Acr )‐induced reduction in mitochondrial membrane potentiality (ΔΨm). GC‐1 cells were exposed to various concentrations of Acr, or arcolein and 0.1 μm Rap for 6 h, and stained with JC‐1 to measure mitochondrial membrane potential by fluorescence microscopy (a, bar = 200 μm) and flow cytometry (b). Punctate red fluorescence represents the potentially dependent aggregate form of JC‐1 in the mitochondria of healthy cells (polarized mitochondria). Diffuse green fluorescence represents the monomeric form of JC‐1 in the cytosol of unhealthy cells (depolarized mitochondria). Thus, the decrease in Red/Green rate meant decline of ΔΨm. Results showed that there was a dose‐dependent trend, that is, higher concentrations of Acr caused decline of ΔΨm in more cells, but Rap could alleviate Acr‐induced decline of ΔΨm. *P < 0.05, compared to 0 μm Acr. **P < 0.05, compared to 0 μm Acr and 0.1 μm Rap.
