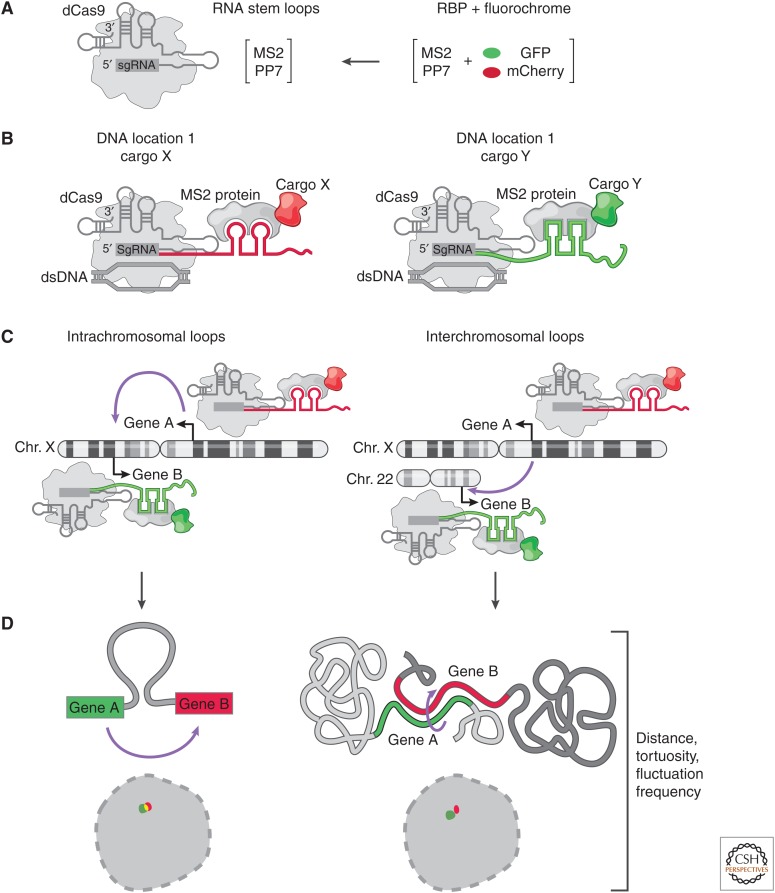
Figure 4.
Live-cell imaging of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) loci. (A) Catalytically inactive CRISPR–Cas9 constructs with extended single-guide RNA (sgRNA) sequences that contain RNA aptamers (e.g., MS2 or PP7). The RNA binding protein (RBP) that recognizes sgRNA aptamers is fused to a fluorescent protein. (B) A CRISPR–dCas9/cargo complex, in which the modified sgRNA specifies the genomic location and acts as a scaffold for delivery of chosen “cargo” fused to the MS2 coat protein. (C) Application of guide sequence aptamer for CRISPR live-cell imaging (CLING). Each guide has a unique RNA aptamer that forms a defined complex with RBP:fluorescent protein fusion. This allows for real-time monitoring of lncRNA loci (or any genomic location) forming intra- or interchromosomal interactions in space and time. (D) Examples of using CLING to monitor the biophysical properties (tortuosity, distance, fluctuation rates) of DNA folding within and across chromosomes.