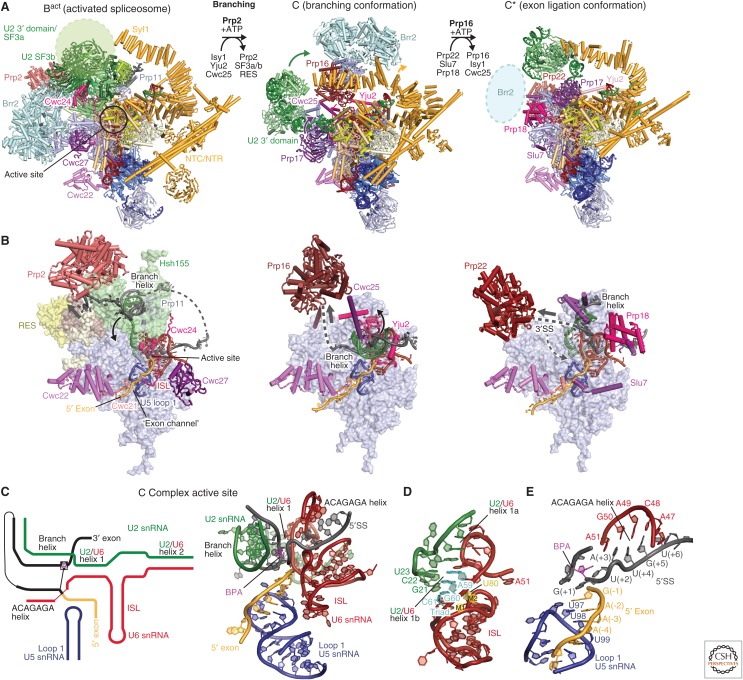
Figure 6.
Branching and spliceosome remodeling. (A) Yeast Bact, C, and C* complex spliceosomes and step-specific factors are required to remodel the spliceosome between these states to move along the splicing pathway. The helicases Prp2 (salmon) and Prp16 (maroon) facilitate the remodeling from Bact to B* for branching and C to C* for exon ligation, respectively. Prp22 (light maroon) facilitates 3′SS proofreading in C* before exon ligation. The three structures, Bact (PDB 5GM6), C (PDB 5JL5), and C* (PDB 5MPS), are aligned using their Prp8 Large domains. (B) The location of the spliceosome active site, step-specific factors and the helicase-mediated remodeling in the Bact, C, and C* complex structures. Although the Bact and C complex structures show Prp2 (red) and Prp16 (dark red), respectively, poised for spliceosome remodeling, the C* structure, which lacks a “docked” 3′SS, reveals instead how Prp22 may contribute to 3′SS proofreading. Prp2 releases the branch helix from the U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle (snRNP) SF3b subcomplex, allowing it to bind in the active site for branching to occur. Prp16 subsequently undocks the branch helix together with step-specific factors Cwc25 and the Yju2 amino terminus, to allow docking of the 3′SS in C*. An arrow indicates the direction of RNA “translocation” (3′-5′ direction) of the helicases, which may remain bound to their respective locations and act at a distance (Semlow et al. 2016). (C) Secondary structure diagram (left) and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure (right) of the RNA-based active site in C complex (PDB 5JL5). This active site conformation is characteristic of all catalytic stage complexes, except for the precise position of the branch helix and remodeling of the ACAGAGA helix. (D) Structure of the U6 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) internal stem loop (ISL) and U2/U6 helix I in C complex. The U2/U6 “catalytic” triad (cyan) and the U6 residue U80 (yellow) coordinate the two catalytic metal ions, which are essential for splicing (M1 and M2, not modeled). (E) Recognition of the precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) 5′ splice site (5′SS) and 5′ exon in the C complex (PDB 5JL5). These interactions remain almost unchanged throughout the catalytic splicing stages.