Figure 3.
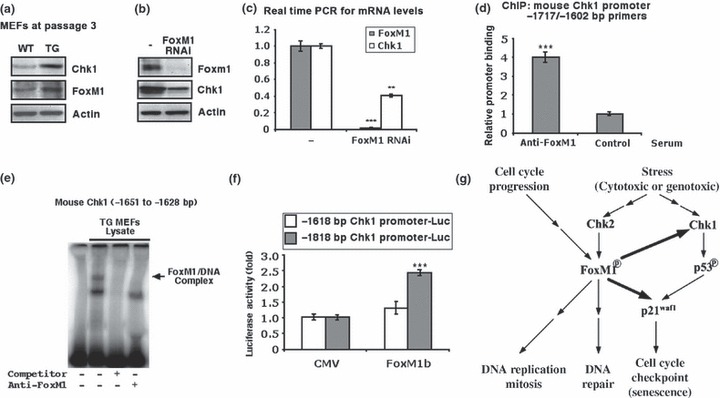
FoxM1 stimulates Chk1 expression and participates in cellular stress responses. (a) FoxM1 TG MEFs display increased protein levels of Chk1. Cell extracts were prepared from WT or TG MEFs at passage 3, and levels of Chk1 (top), FoxM1 (middle) and β‐actin (bottom) were analysed by western blotting. (b and c) FoxM1‐depleted human osteosarcoma U2OS cells exhibit reduced expression of Chk1 mRNA and protein. U2OS cells were transfected with FoxM1 siRNA or control siRNA and 72 h later, protein and RNA were prepared to examine for the expression of Chk1 or FoxM1 protein by western blotting (b) and Chk1 or FoxM1 mRNA using qRT‐PCR (c). (d) ChIP assays show direct binding of FoxM1 to the endogenous mouse Chk1 promoter regions. WT MEF chromatin was cross‐linked, sonicated, and then IP with either FoxM1 antiserum or rabbit serum (control) was performed, and the amount of promoter DNA associated with the IP chromatin was quantified using qRT‐PCR with primers specific to the mouse Chk1 promoter region. (e) FoxM1 bound to Chk1 promoter. Nuclear extract was prepared from FoxM1 TG MEFs and used for EMSA with a 32P‐labelled DNA probe synthesized from the mouse Chk1 promoter sequence position −1651 to −1628 bp. (f) The mouse Chk1 −1818 bp promoter is stimulated by FoxM1. Cotransfection assays were performed in mouse hepatoma Hepa1‐6 cells with the CMV‐FoxM1b expression vector and luciferase plasmid containing −1818 or −1616 bp of the mouse Chk1 promoter region, prepared protein extracts at 24 h after transfection, and used them to measure dual luciferase enzyme activity. In this figure the asterisks indicate statistically significant changes: **P ≤ 0.01 and ***P ≤ 0.001. (g) Model of the function of FoxM1 in response to cellular stress. The FoxM1 transcription factor regulates the expression of cell cycle genes essential for progression into DNA replication and mitosis. In response to genotoxic stress, Chk2 phosphorylates and stabilizes the FoxM1 protein and increased levels of FoxM1 activate the transcription of the DNA repair genes (33). In this study, modestly increased levels of FoxM1 in normal cells (MEFs) stimulate the expression of Chk1 that phosphorylates and activates p53. FoxM1 also stimulates p21 expression in concert with p53 and enhances the senescent phenotype during passaging MEFs. Stress signalling also induces DNA repair enzymes and cell cycle checkpoint independent of the FoxM1 transcription factor (not shown in the figure).
