Figure 4.
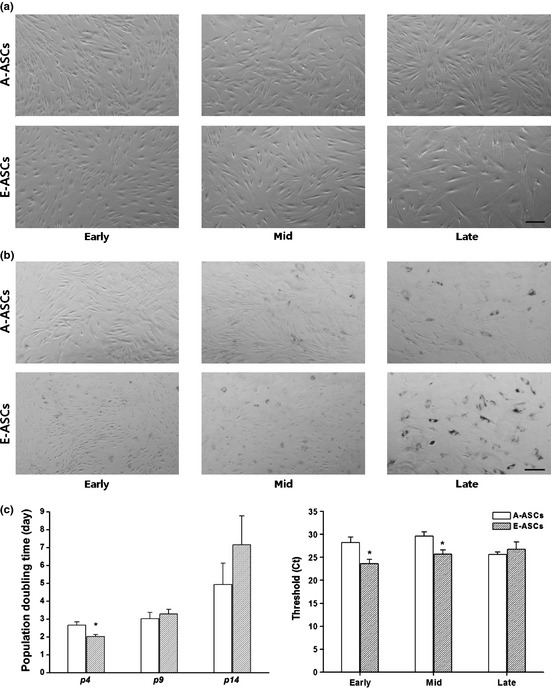
Characterization of the A‐ASCs and E‐ASCs during long‐term culture in vitro. (a) Morphological change due to repetitive subculture. Scale bar: 200μm. (b) Senescence‐associated β‐galactosidase activity of both ASCs at early‐, mid‐, and late‐passage. Scale bar: 200 μm. (c) Population doubling (PD) time of the early‐, mid‐, and late‐passage cells. The PD time of the early‐passage (p4) E‐ASCs was shorter than that of A‐ASCs (P < 0.05) at the same age; however, the time of the late‐passage (p14) E‐ASCs became longer than that of the A‐ASCs at the same age. (d) Telomerase activity of ASCs at the early‐, mid‐, and late passage by qRT‐PCR. Ct values of E‐ASCs at early‐ and mid‐passage were significantly lower than Ct values of A‐ASCs at the same ages.
