Figure 6.
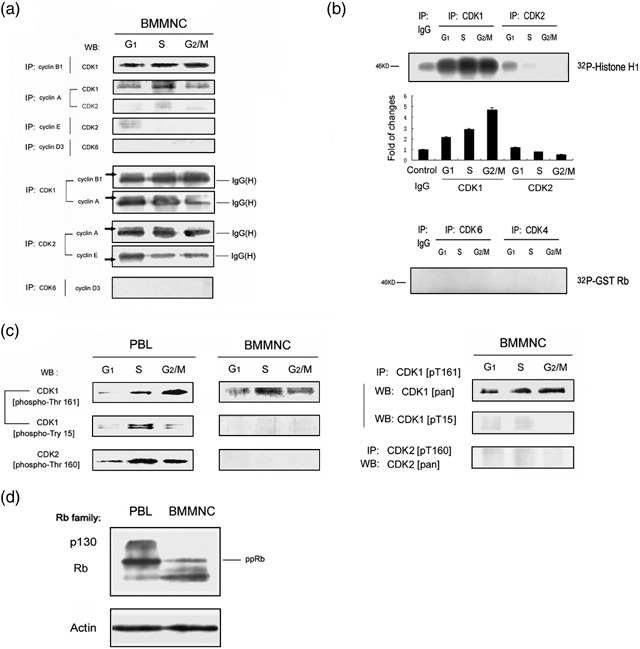
Activation of Cdk‐associated kinase during the bone marrow cell cycle. (a) Molecular analysis of cyclins association with Cdks within different cell‐cycle phases in BMMNC. Freshly isolated BMMNC were flow‐sorted based on DNA content and distribution. G1, S and G2/M phase cell lysates were prepared and immunopreciapitation (IP)–Western blotting (WB) analysis of cyclins and Cdks are shown. (b) Cdk‐associated kinase activity during different cell cycle phases in BMMNC. Freshly isolated BMMNC were flow‐sorted based on DNA content. G1, S and G2/M phase cell lysates were prepared. Cdks 1, 2, 4 and 6 were immunoprecipitated and activity to histone H1 or GST‐Rb was measured. (c) Molecular analysis of phosphorylation states of Cdk1‐ and Cdk2‐specific residues in BMMNC versus cultured PBL. G1, S and G2/M phase cells were flow‐sorted based on DNA content. Cell lysates were immunoblotted and probed with the appropriate anti‐CDK1[pT161] antibody, anti‐CDK1[pT15] antibody, and anti‐CDK2[pT160] antibody (left). BMMNC cell lysates from G1, S and G2/M phase cells were also immunoprecipitated with anti‐CDK1[pT161] or anti‐CDK2[pT160] antibody, then probed with anti‐CDK1[pan], anti‐CDK1[pT15] antibody or anti‐CDK2[pan] antibody (right). (d) Lysates prepared from freshly isolated BMMNC, and exponentially cultured PBL were immunoblotted and probed with Rb antibody.
