Figure 7.
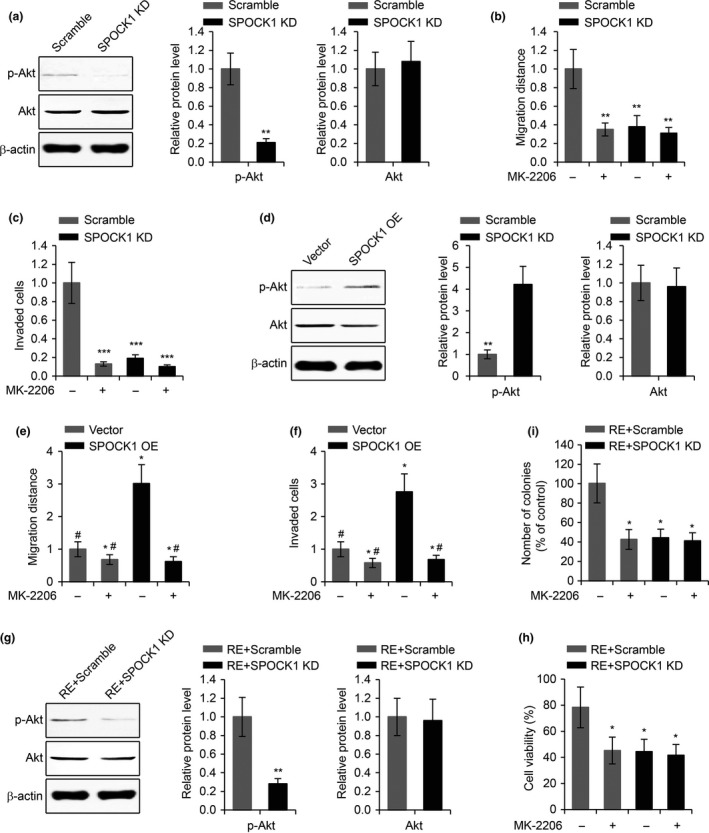
SPOCK1 regulates GBM cell invasion and TMZ resistance via the Akt pathway. (a) Western blot of phosphorylated Akt (p‐Akt) and total Akt levels in U87 cells transfected with scramble siRNA or SPOCK1 siRNA (SPOCK1 KD). p‐Akt and total Akt levels related to β‐actin were quantified in right panel. (b) Wound healing cell migration assay and (c) transwell cell invasion assay in U87 cells transfected with scramble siRNA or SPOCK1 siRNA (SPOCK1 KD) subjected to the treatment of Akt inhibitor MK‐2206. (d) Western blot of phosphorylated Akt (p‐Akt) and total Akt levels in U87 cells transfected with empty vector or plasmid overexpressing SPOCK1 (SPOCK1 OE). (e) Wound healing cell migration assay and (f) transwell cell invasion assay in U87 cells transfected with empty vector or plasmid overexpressing SPOCK1 (SPOCK1 OE) subjected to the treatment of Akt inhibitor MK‐2206. (g) Western blot of phosphorylated Akt (p‐Akt) and total Akt levels in TMZ‐resistant U87 cells transfected with scramble siRNA (RE+scramble) or SPOCK1 siRNA (RE+SPOCK1 KD). (h) MTT cell viability assay and (i) colony formation assay in TMZ‐resistant U87 cells transfected with scramble siRNA (RE+scramble) or SPOCK1 siRNA (RE+SPOCK1 KD) subjected to the treatment of Akt inhibitor MK‐2206. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.01 compared to scramble or empty vector control cells. #P < 0.05 compared to SPOCK1 OE cells without MK‐2206 treatment.
