Figure 5.
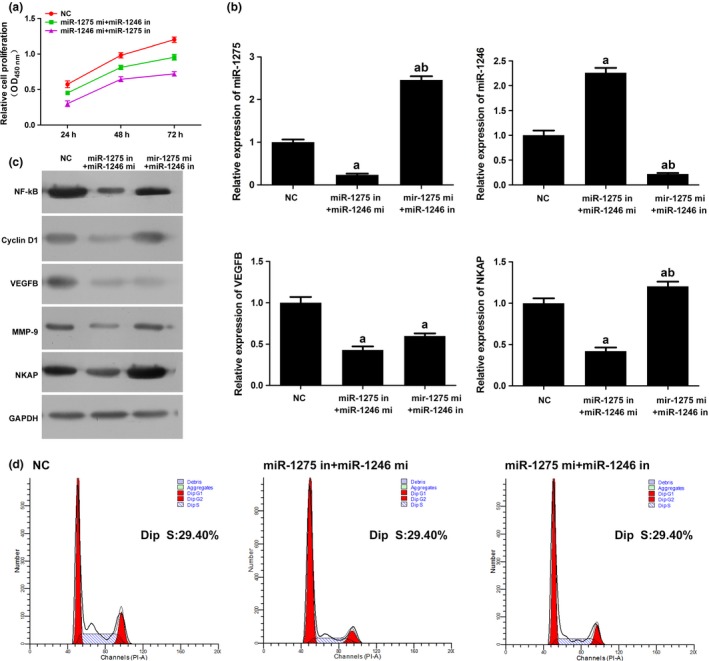
MiR‐1275 and miR‐1246 affect the proliferation of HUVECs synergistically via NF‐κB signalling. (a) Cell viability of HUVECs was inhibited by concatenated administration of mimics and inhibitors of the two miRs. Moreover, miR‐1245 mimics could confound the effect of miR‐1275 inhibitor to some extent. (b) Quantitative analysis results of the expression levels of miR‐1275, miR‐1246, VEGFB and NKAP in HUVECs as detected by qRT‐PCR (U6 was employed as an internal reference gene for miR‐1275 and miR‐1246, and β‐actin was employed as an internal reference gene for VEGFB and NKAP). Administration of concatenated administration of mimics and inhibitors of the two miRs inhibited the expression of all the molecules. MiR‐1245 mimics could confound the effect of miR‐1275 inhibitor on the expression of VEGFB to some extent. (c) Representative images of the expression levels of NF‐κB, Cyclin D1, VEGFB, MMP‐9, NKAP in HUVECs as detected by Western blotting. Administration of concatenated administration of mimics and inhibitors of the two miRs inhibited the expression of all the molecules. MiR‐1245 mimics could confound the effect of miR‐1275 inhibitor to some extent. (d) Representative images of cell cycle distribution as detected by flow cytometry. Administration of concatenated administration of mimics and inhibitors of the two miRs decreased the number of cell distributed in S phase. MiR‐1245 mimics could confound the effect of miR‐1275 inhibitor to some extent. “a,” Significantly different from NC group, P<.05. “b,” Significantly different from 1275 mimics group, P<.05. “c,” Significantly different from 1246 mimics group, P<.05
