Figure 2.
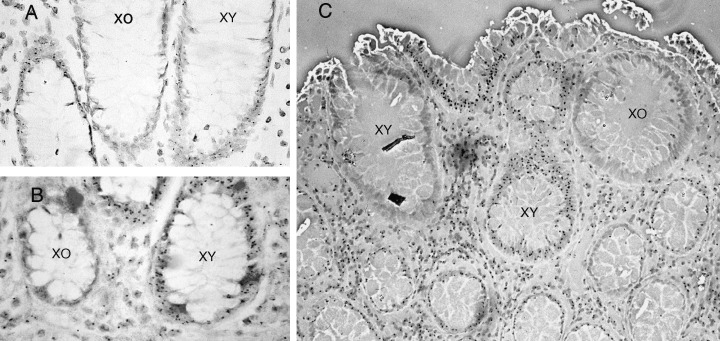
Monoclonal origins of human colonic crypts. Normal colonic mucosa from a rare XO/XY patient with FAP (a, b). Crypts stained by in situ hybridization with a Y chromosome‐specific probe, either stain positively or negatively for the Y chromosome (small black dot within XY cells). (c) Polyclonal adenoma in the same chimeric patient, with a mixture of XO and XY crypts. Reprinted with permission from Preston et al (2003).
