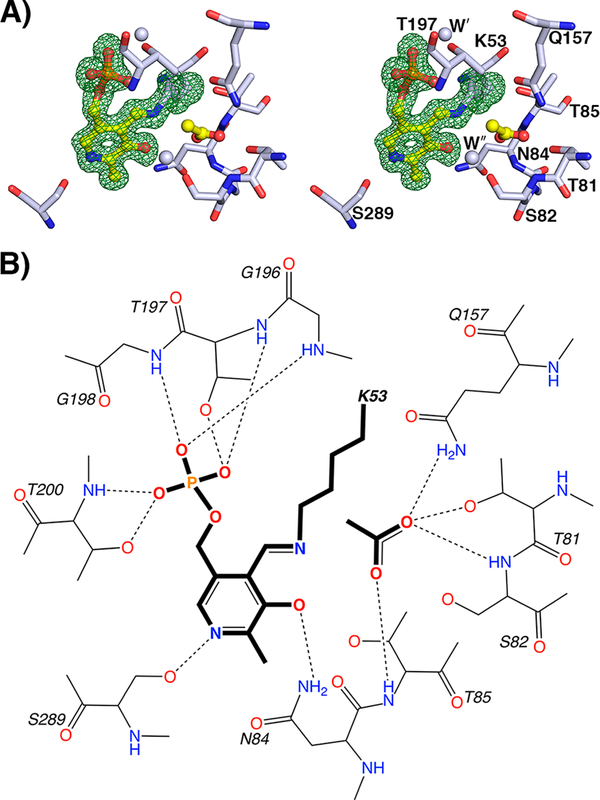
Figure 4.
The yCBS catalytic core active site. (A) PLP is held in the active site as an internal aldimine formed by a Schiff base linkage with K53. The Fobs – Fcalc electron density contoured at 3σ from a simulated annealing omit map is shown in green. An acetate ion has been modeled into the active site and is held in place by interactions with residues 81–84. The carboxylate groups of the E-PLP-l-ser and E-PLP-aa intermediates are similarly coordinated (Figure 5). Atoms are colored according to element as follows: gray, carbon; blue, nitrogen; red, oxygen; orange, phosphorus. The carbon atoms of PLP and acetate are colored yellow. (B) Schematic diagram of the yCBS-cc active site. Hydrogens are shown for side-chain and backbone amide groups only because their locations can be defined chemically, whereas those of side-chain hydroxyl groups, especially those involved in hydrogen bonds, cannot. Distances for key interactions between atoms are reported in Table S2.