Figure 5. RNA binding and limited proteolysis of SpyCas9WT and SpyCas92Pro.
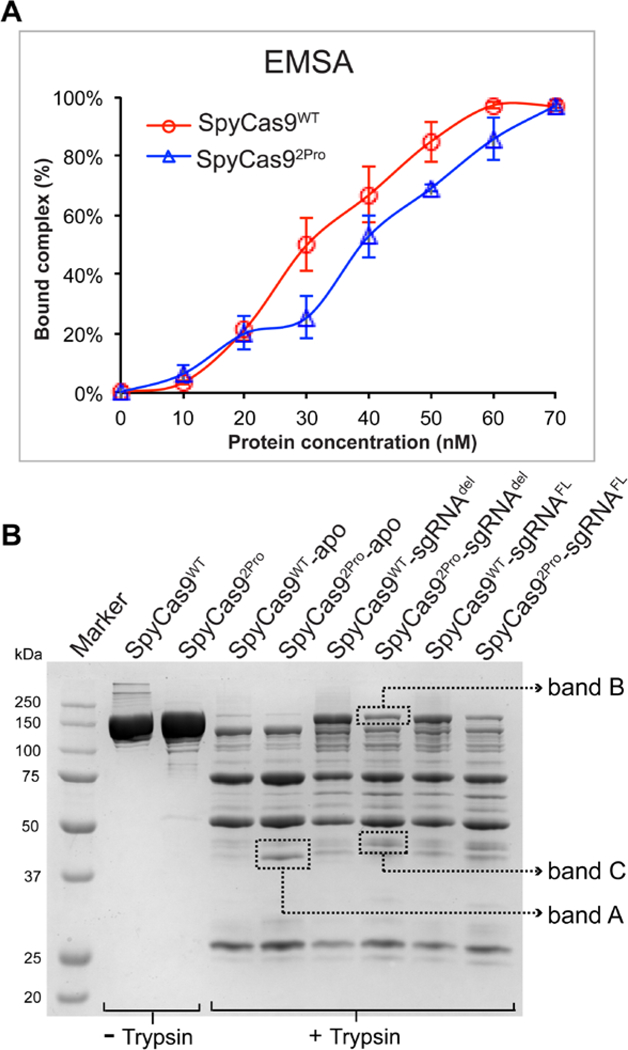
A) Graph showing quantification of binary complex formed by SpyCas92Pro and SpyCas9WT. EMSA was conducted using 5’−32P labelled sgRNAdel. The protein concentration was increased from 10 nM to 70 nM relatively to sgRNA concentration (~50 nM). Graph shows the average of bound complex from three independent replications over different protein concentrations. The data indicate that the RNA binding property of SpyCas92Pro is not significantly reduced compared to SpyCas9WT. B) Trypsin digestion of SpyCas9WT and SpyCas92Pro with or without sgRNA. In the apo-form, the digestion profiles for both proteins are similar except for increased intensity of Band A in SpyCas92Pro. The sgRNA bound form of SpyCas92Pro is not protected to the same extent as SpyCas9WT-sgRNA complex (see the difference in intensity of Band B). In addition, Band C is more prominent in SpyCas92Pro-sgRNA complex, indicating conformational differences between the two binary complexes.
