Table 1.
Inhibitory effect of the synthesized compounds on influenza virus-infected MDCK cellsa.
 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Compd. | Structure | Activity (EC50, μM)b |
MCC (μM)c |
| 1 | 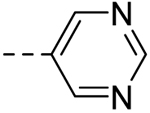 |
−d | >100 |
| 2 | 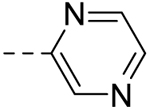 |
− | >100 |
| 3 | 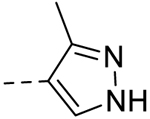 |
− | >100 |
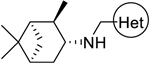
| 4 | 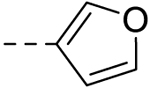 |
60.46 ± 1.75 | >100 |
| 5 | 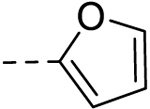 |
− | 50 |
| 6 | 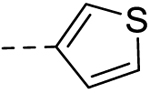 |
28.60 ±0.24 | 50 |
| 7 | 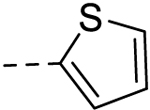 |
6.42 ± 0.18 | 25 |
| 8 | 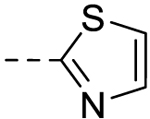 |
− | >100 |
| 9 | 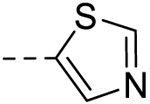 |
− | >100 |
| 10 | 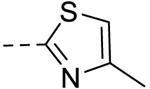 |
75.00 ± 0.08 | >100 |
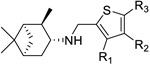 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R2 | R3 | |||
| 11 | Me | H | H | − | 10 |
| 12 | Et | H | H | − | 25 |
| 13 | Br | H | H | − | 50 |
| 14 | n-Pr | H | H | − | 50 |
| l5 | n-Bu | H | H | 10.33 ± 2.17 | 25 |
| 16 | OEt | H | H | − | 50 |
| 17 | vinyl | H | H | 1.82 ± 1.04 | 50 |
|
18 (M090) |
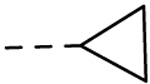 |
H | H | 0.30 ± 0.04 | 25 |
| l9 | 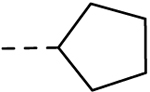 |
H | H | 0.69 ± 0.12 | 12.5 |
| 20 | 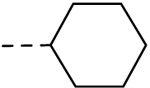 |
H | H | − | 1.56 |
| 21 | 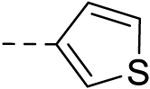 |
H | H | − | 12.5 |
| 22 | 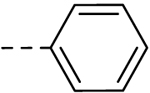 |
H | H | − | 12.5 |
| 23 | H | Br | H | 5.16 ± 1.08 | 6.25 |
| 24 | H | Me | H | 0.20 ± 0.004 | 12.5 |
| 25 | H | Et | H | − | 25 |
| 26 | H | n-Pr | H | − | 12.5 |
| 27 | H | n-Bu | H | 0.46 ± 0.07 | 12.5 |
| 28 | H | vinyl | H | − | 6.25 |
| 29 | H | 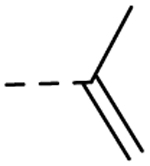 |
H | − | 25 |
| 30 | H | 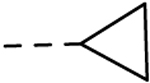 |
H | 6.68 ± 0.42 | 25 |
| 31 | H | 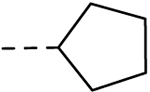 |
H | − | 1.56 |
| 32 | H | 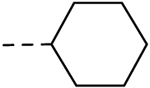 |
H | − | 0.78 |
| 33 | H | 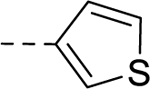 |
H | − | 25 |
| 34 | H | 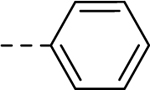 |
H | − | 5 |
| 35 | H | H | Cl | − | 25 |
| 36 | H | H | Me | − | 0.78 |
| 37 | H | H | Br | − | 43 |
| 38 | H | H | Et | − | 1.56 |
| 39 | H | H | t-Bu | − | 0.78 |
| 40 | H | H | 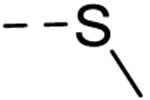 |
− | 25 |
| 41 | H | H | 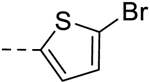 |
− | 0.78 |
| Amantadine | >100 | >100 | |||
Virus strain, A/Guangzhou/GIRD/07/2009 (H1N1).
All the compounds were also tested for the inhibitory effect against A/WSN/33 and A/HK/68 strains based on a CCK-8 reagent measurement method44. Compounds 6, 7, 10, 11–18, 23, 24, 26, 28, 30, 36 and 40 exhibited range of micromolar to sub-micromolar activity against both strains (the data were not shown), consistent with this experiment with the Guangzhou strain, compound 18 (M090) was the most potent inhibitor of the WSN and HK strains too.
MCC: minimum cytotoxic concentration, or concentration which led to minimal change in cell morphology after 48 h incubation with compound.
“−” represent that no viral inhibition occurs when the concentrations of compounds were lower than MCC.
