Figure 3.
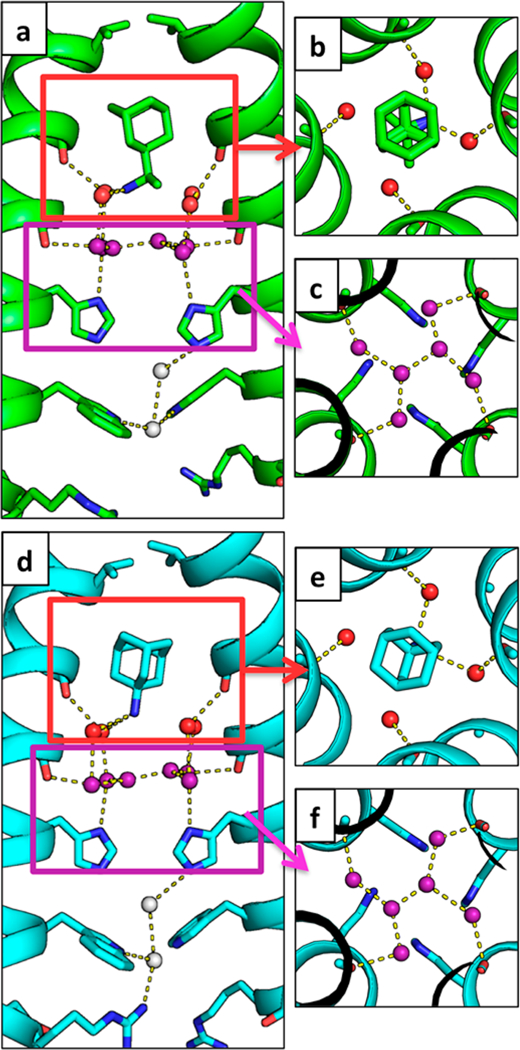
Water-mediated hydrogen bonds facilitate the binding of rimantadine and amantadine to the M2 pore. In both the rimantadine- bound (6BKL, green) and amantadine-bound (6BKK, cyan) structures of the Inwardclosed conformation, the drug ammonium group is positioned to hydrogen-bond with two of the four waters in the Ala30 water layer, shown as red spheres. The Gly34 water layer is shown as purple spheres. Hydrogen bonds are shown as yellow dashes. Amantadine and rimantadine bind asymmetrically and form hydrogen bonds with two of the four waters in the top solvent layer. (a, d) Side views of binding of rimantadine (a, monomer subunits F and H) and amantadine (d, monomers B and D). (b, e) Top-down views of binding of rimantadine (b, monomers E-H) and amantadine (e, monomers A-D) to the Ala30 water layer in the pore of the M2 channel. (c, f) Top-down views of the Gly34 water layer.
