Figure 1. Characterization SMA- EA:DMPC nanodisc:
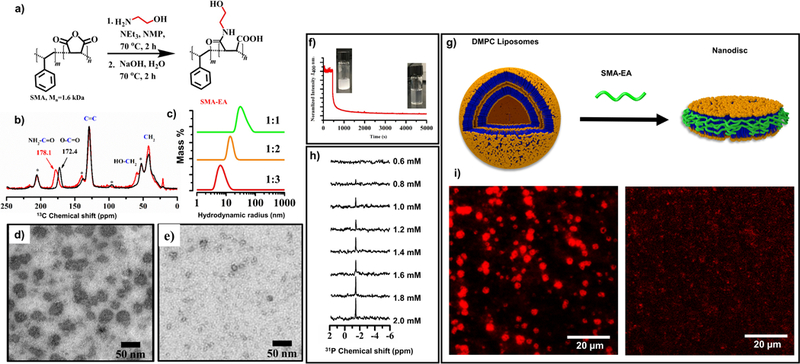
A) Reaction scheme used for the synthesis of SMA-EA. b) Characterization of SMA-EA by 13C CP- MAS NMR: SMA (black) and SMA- EA (red); spectra were obtained under 8 kHz spinning speed. TEM images of nanodiscs obtained from DMPC:SMAEA (1:1 w/w) (d) and DMPC:SMAEA( 1:3 w/w) (e). (f) Normalized Static light scattering showing the solubilization of large DMPC MLVs in to smaller particles after the addition of SMA-EA polymer, inset showing the increase in the transparency of the solution. (g) Schematic showing the formation of nanodiscs. (h) 31P NMR spectra showing the appearance of an isotropic peak after the polymer addition indicating the formation of small size nanodiscs that tumble fast on the NMR time scale. (i) TIRF images showing the solubilization of 1 mol % of rhodamine- functionalized DMPE (1,2- Dimyristoyl- sn- glycero- 3- phosphoethanolamine) containing DMPC MLVs by the addition of the SMA-EA polymer: before (left) and after (right) the addition of SMA-EA. (This Figure was adapted with permission from Ravula et al., 2017b)
