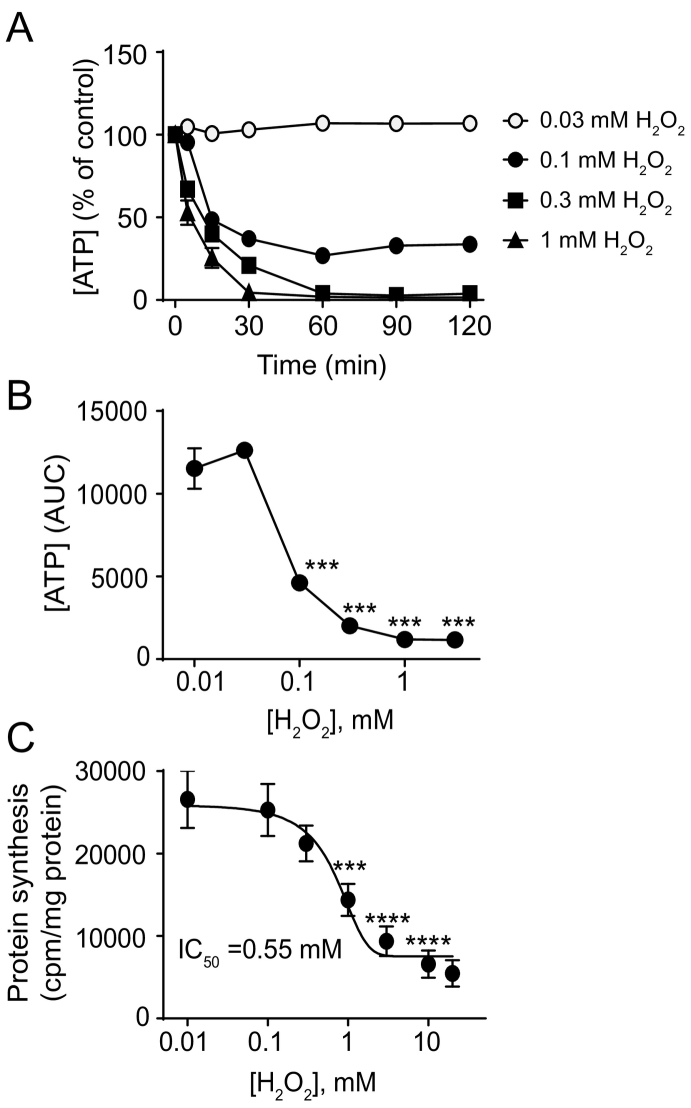
Fig. 1.
H2O2 reduces ATP levels and inhibits protein synthesis in cardiomyocytes. Cardiomyocytes were exposed to the concentrations of H2O2 shown for the times indicated. (A) Concentrations of ATP were measured using a luciferase assay. Results are % of control values and are means ± SEM (n = 4 independent myocyte preparations). (B) Area under curve (AUC) analysis of cardiomyocyte ATP levels from the data in (A). ***p < .001 relative to control (one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test). (C) Protein synthesis was measured by incorporation of [3H]-Phe. Results are means ± SEM (n = 4 independent myocyte preparations). The IC50 was calculated using the 4-step parameter function in GraphPad Prism 7. ***p < .001, ****p < .0001 relative to 0.1 mM H2O2 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test).