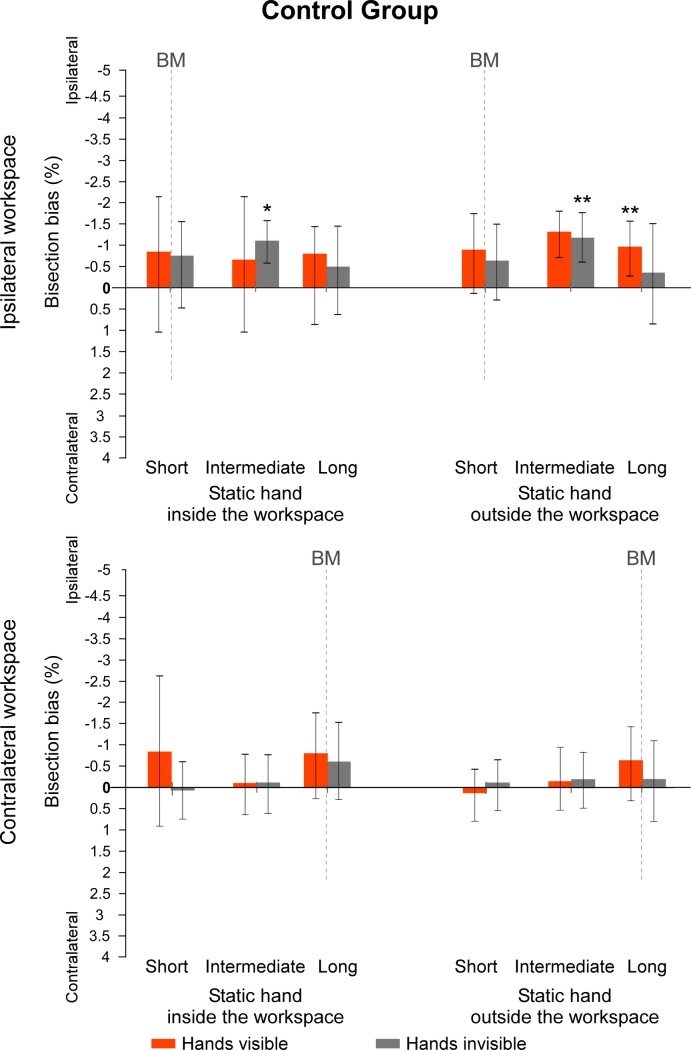
Fig 6. Mean bisection biases made by the control participants (hemibody code).
Values represent the mean differences between the estimation of the participants and the real midpoint of the lines, according to each of the workspace, position of the static hand, vision of the hands and line distance (short vs. intermediate vs. long) conditions. Direction of the bisection biases are coded relatively to the static hand (i.e. ipsi- vs. contralateral). Note that the line length factor is not represented in this figure. Dash lines at 0 cm correspond to the vertical median of the semi-reflexive screen to which participant’s body midline (BM) was aligned. The values of the two sub-groups defining which hand was used to perform the bisection were merged together. Values are expressed in terms of percentage of the total length of the lines. Negative values indicate ipsilateral biases and positive values contralateral biases. Error bars indicate the 95% confidence intervals adapted according to the method of Cousineau [36]. Asterisks illustrate the t-tests against zero that reach significance level (* .05 ≥ p > .01, ** p ≤ .01).