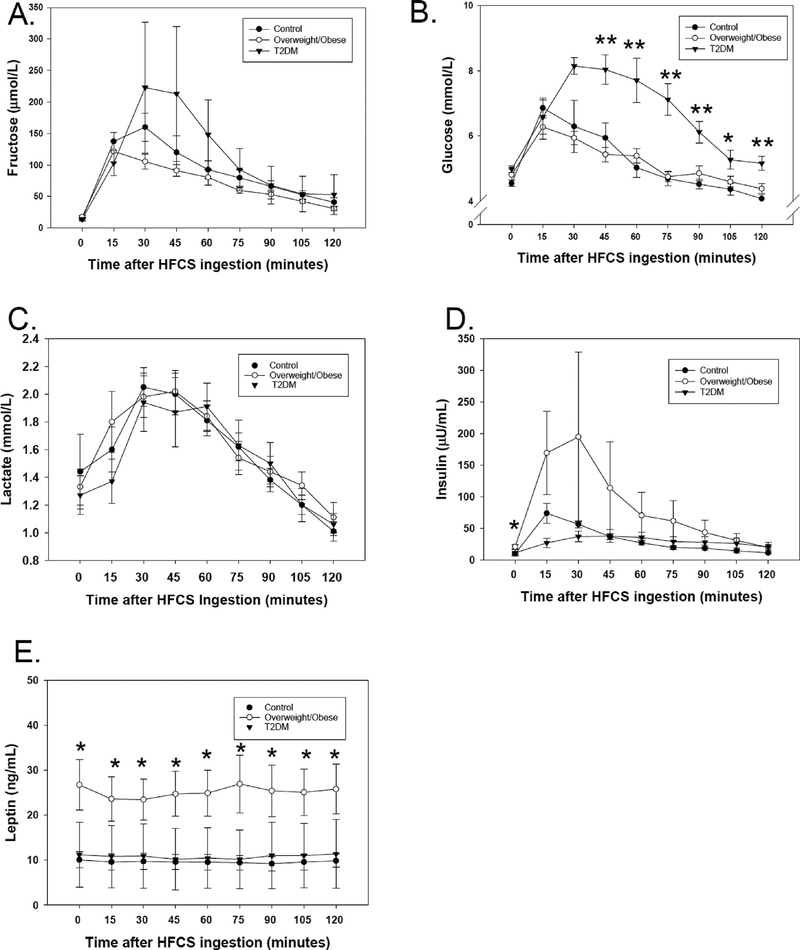
Fig. 1.
Fructose, glucose, lactate, insulin, and leptin concentrations at baseline, and at multiple time points over 120 min after high fructose corn syrup (HFCS) soda ingestion. Subjects who are lean controls are represented by filled circles, subjects with overweight/obesity are represented by open circles, and subjects with T2DM are represented by filled inverted triangles. The mean and standard error of the mean at each time point are shown. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 in comparison of the three groups by ANOVA. A. Fructose concentrations (μmol/L) rose after HFCS consumption and remained higher than baseline at every time point but did not significantly differ among groups. B. Glucose (mmol/L) was significantly higher among T2DM subjects after HFCS ingestion from 45 to 120 min. C. Lactate (mmol/L) rose non-significantly after HFCS consumption but did not differ among the three groups. D. Insulin (1μIU/mL = 7.175 pmol/L) was significantly higher in overweight/obese subjects at baseline. E. Leptin (ng/mL) did not change after HFCS consumption, but was significantly higher in the overweight/obese group across all time points.