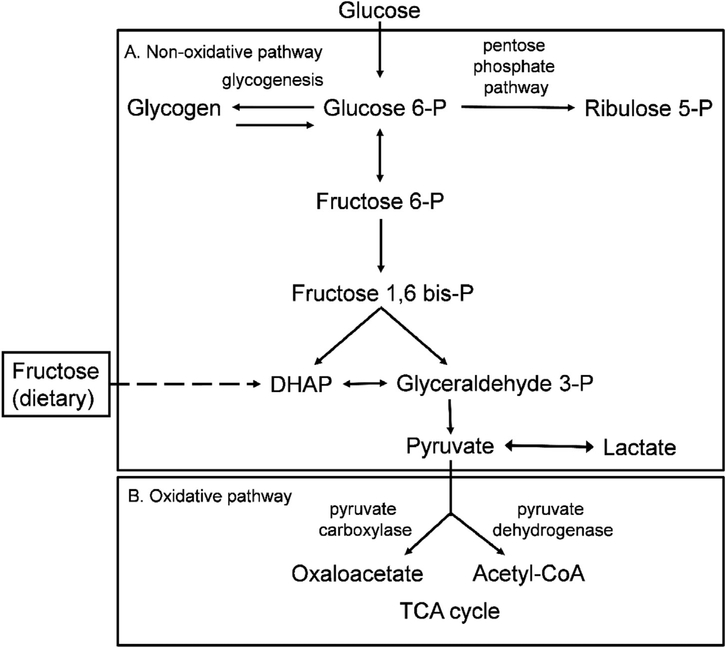
Fig. 2.
Non-oxidative and oxidative pathways of carbohydrate metabolism. A. The non-oxidative pathway of glycolysis. Glucose is converted to glucose-6-phosphate (glucose-6-P) which may be used as a substrate in the pentose phosphate pathway for pyrimidine synthesis, or continue down glycolysis to be converted to pyruvate. Lactate may be formed from pyruvate under anaerobic conditions. Dietary fructose is converted to fructose-1-phosphate, which then enters glycolysis through production of dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP). B. Pyruvate enters the oxidative steps of the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) to produce acetyl CoA via pyruvate dehydrogenase or oxaloacetate through pyruvate carboxylase.