Fig. 4.
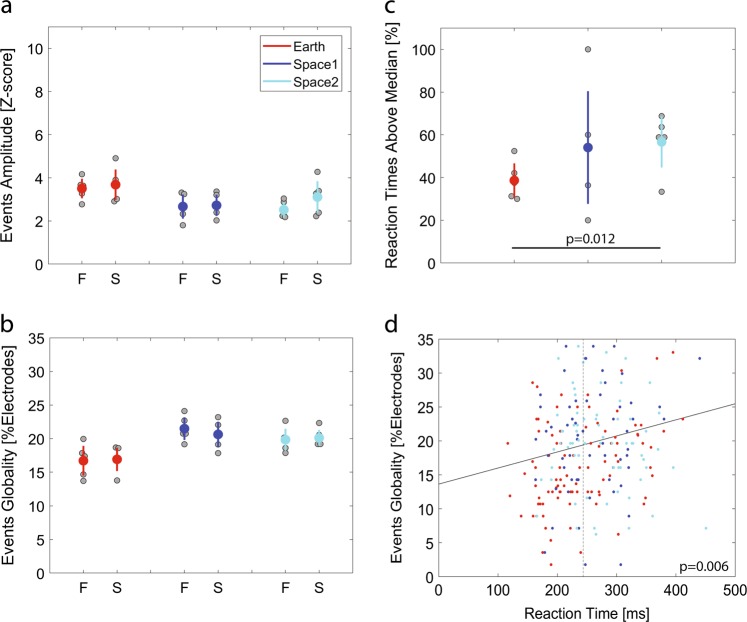
Local sleep-like events impact on cognitive tasks and alertness. a, b During the 10 s of the recovery manoeuvre, the astronauts either Failed (F) or Succeeded (S) to dock the simulated Soyuz vehicle. The two outcomes of the visuomotor task could not predict the local sleep-like events’ properties. Each grey dot represents the mean value for one astronaut and the mean ± sem across astronauts are colour marked as a dot and a line, respectively. c Reaction time until first movement while performing the recovery manoeuvre. There is a higher percentage of above median reaction times in space2 compared to Earth. d The full line illustrates the positive correlation between the local sleep-like events’ globality around the starting point of the recovery manoeuvre (−250 ms to 500 ms) and the reaction times across all trials. The median reaction time is marked by a dotted line at 244 ms. (n = 5 astronauts)