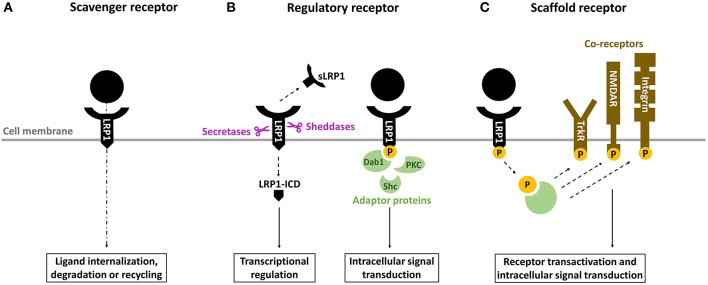
Figure 2.
Overview of the biological properties of LRP1. (A) as a scavenger receptor, LRP1 binds and internalizes a wide range of ligands for degradation in lysosomes or recycling. (B) as a regulatory receptor, LRP1 modulates gene transcription through its intracellular domain (LRP-ICD) generated by intramembrane proteolysis and releases its extracellular ectodomain (soluble LRP [sLRP1]) in the circulation, where it exerts numerous biological functions. Alternatively, LRP1-ICD has the ability to recruit various adaptor proteins to transduce multiple intracellular signals. (C) as a scaffold receptor, LRP1 modulates the activity of other membrane proteins including integrins, tyrosine kinase (Trk) receptors and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors.