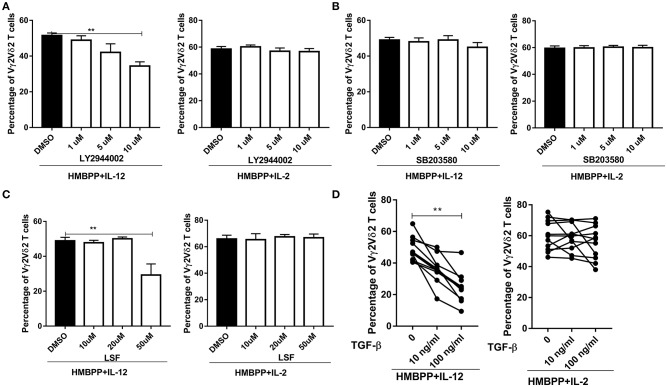
Figure 4.
Both PI3K/AKT and STAT4 pathways, but not p38/MAPK, are involved in the IL-12-induced expansion of HMBPP-activated Vγ2Vδ2 T cells. (A–C) are graph data showing that PI3K/AKT and STAT4, but not P38/MAPK pathway, were required for HMBPP + IL-12 expansion of Vγ2Vδ2 T cells was reduced by the chemical blockers for PI3K/AKT and STAT4 pathways, but not those for P38/MAPK. PBMCs were co-cultured for 7 days with HMBPP + IL-2 or HMBPP + IL-12 in the presence of escalating doses (1, 5, 10 μM) of LY2944002 (inhibitor for PI3K/AKT), SB203580 (inhibitor for p38/MAPK), or doses (10, 20, 30, 40, 50 μM) of LSF (inhibitor for STAT4) or DMSO. Data are mean ± SEM of three independent experiments pooled from 12 healthy controls. **p < 0.01, vs. media group (ANOVA, Dunnett's test). (D) Exogenous TGF-β significantly reduce the ability of IL-12, but not IL-2, to expand HMBPP-activated Vγ2Vδ2 T cells. TGF-β (10 or 100 ng/ml) was added to the PBMC cultures treated with HMBPP + IL-12 or HMBPP + IL-2 (n = 12), and cells were cultured for 7 days prior to the flow-based analysis of the expansion of Vγ2Vδ2 T cells. Each dot represents one healthy control. **p < 0.01 vs. control group (paired t-test).