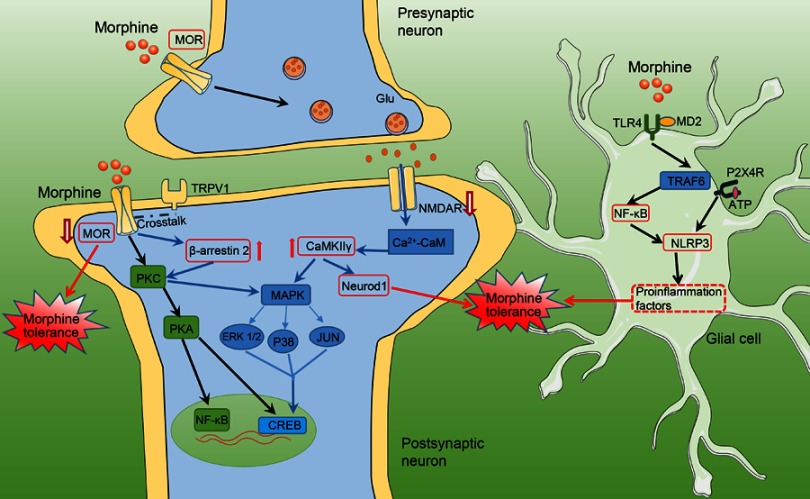
Figure 1.
Schematic showing mechanisms underlying morphine tolerance. Schematic model showing how MOR/β-arrestin 2 and NMDAR/CaMKⅡγ-dependent signaling in neuron plays a crucial role in the promotion of morphine tolerance. Morphine induces activation of glial cells and upregulates proinflammatory cytokines via the TLR4/NF-κB pathway to facilitate morphine tolerance.
Abbreviations: MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; NeuroD 1, neurogenic differentiation factor 1; TRAF6, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6; P2X4R, purinergic P2X4 receptors; ATP, adenosine 5'-diphosphate; NLRP3, NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 inflammasome.