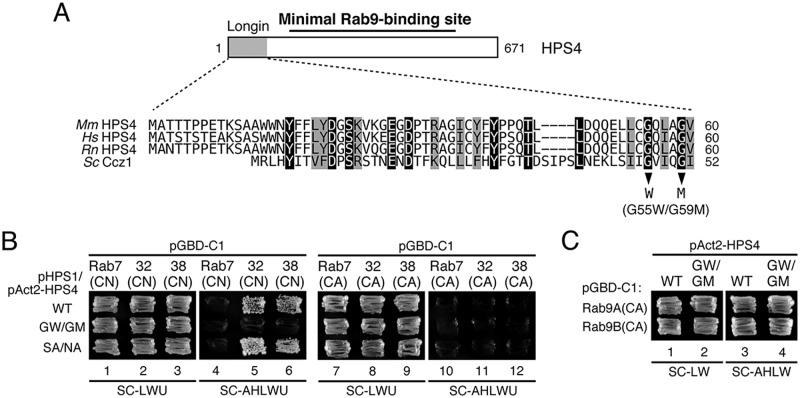
Figure 5.
Identification of critical residues responsible for the Rab32/38-GEF activity of HPS4 by site-directed mutagenesis. A, sequence alignment of the longin domain of mouse (Mm), human (Hs), and rat (Rn) HPS4 and yeast Ccz1. Identical residues and conserved residues in HPS4 are shown against a black background and gray background, respectively. Two Gly residues, Gly-47 and Gly-51, in yeast Ccz1 have been shown to be essential for Ypt7-GEF activity (27), and the corresponding Gly residues were also conserved in mammalian HPS4 and were the focus of the site-directed mutagenesis to create Rab32/38-GEF activity–deficient HPS4. B, Rab32/38(CA/CN) binding activity of BLOC-3 (HPS1/4) WT and mutants as revealed by yeast tri-hybrid assays. Yeast cells containing pHPS1 plasmids, pAct2 plasmids expressing HPS4(WT or mutants), and pGBD-C1-Rab7/32/38(CA/CN)ΔCys plasmids were streaked on SC-LWU (lacking leucine, tryptophan, and uracil) or SC-AHLWU (lacking adenine, histidine, leucine, tryptophan, and uracil) medium (selection medium) and incubated at 30 °C. C, the normal Rab9 binding activity of HPS4(G55W/G59M) (GW/GM). Two-hybrid assays were performed as described for Fig. 3B.