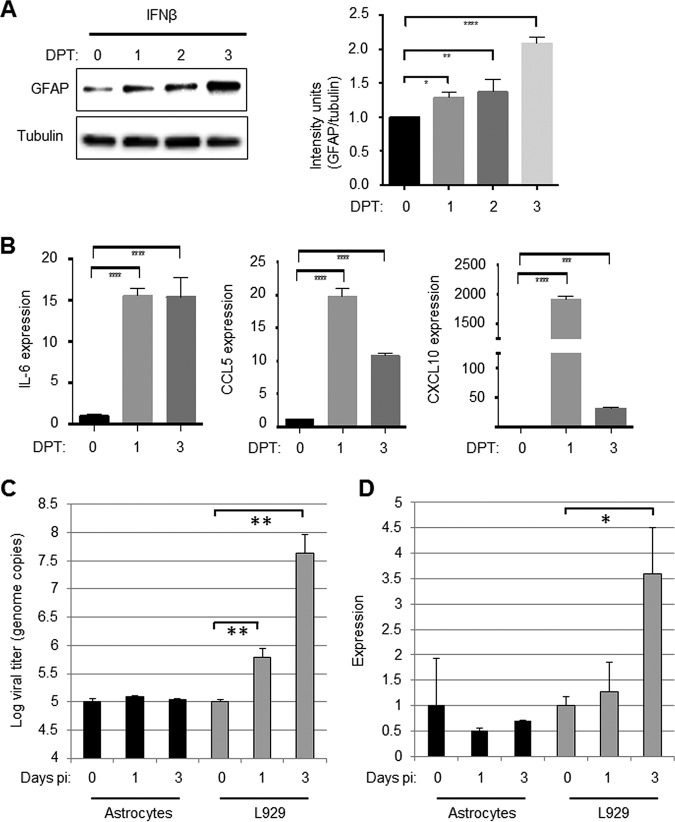
FIG 4.
Treatment with IFN-β activates primary astrocytes. Primary astrocytes were treated with IFN-β (100 U/ml). At 0, 1, 2, and 3 days posttreatment (DPT), the cells were harvested for Western blot analysis. (A) A representative blot shows that IFN-β treatment causes increased expression of GFAP in primary astrocytes. The graph shows combined data from three blots and demonstrates significant increases in relative intensity of GFAP staining in astrocytes treated with IFN-β. (B) Astrocytes were also collected for RT-PCR analysis. The graphs show the mean expression of chemokines/cytokines associated with astrocyte activation in IFN-β-treated and untreated astrocytes. (C) Astrocytes were infected with reovirus (MOI of 1). At 0, 1, and 3 days p.i., RNA was harvested from infected cells, and the viral titer was determined by quantitative PCR that was compared to a standard curve. The graph shows the mean viral titer in astrocytes immediately after infection (day 0) and after 1 and 3 days (black bars). Reovirus titers in L929 cells that were infected in parallel are shown for comparison (gray bars). (D) RNA from reovirus-exposed astrocytes was assayed for the presence of IFN-β RNA. The graph shows the mean expression compared to day 0 (black bars). Reovirus induced expression of IFN-β in L929 cells is shown for comparison (gray bars). All error bars represent the SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001.