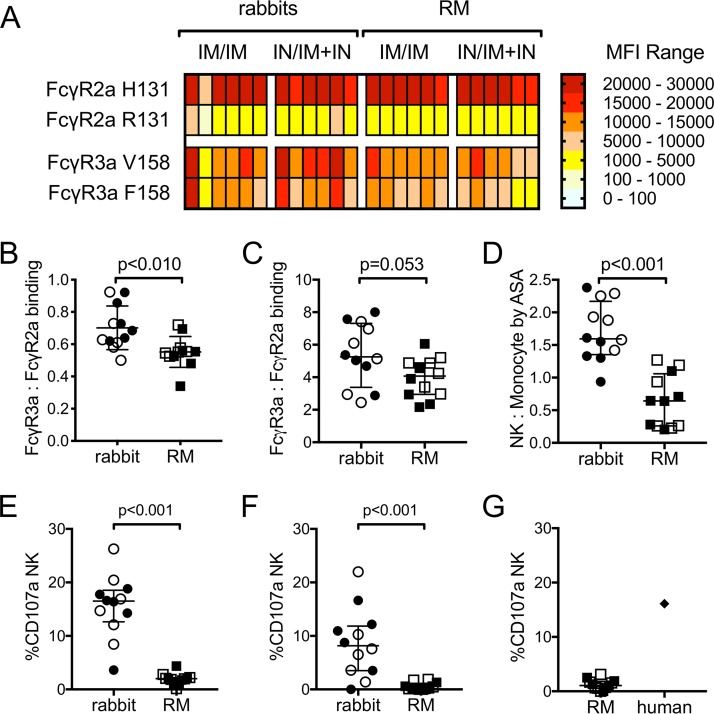
FIG 7.
Vaccine-elicited antibodies from rabbits and rhesus macaques (RM) differentially bind to human FcγR and recruit effector cells. (A) Heat map representing results of multiplexed Fc array performed with rabbit and RM serum samples collected 3 weeks after completion of the vaccine regimens (week 19). Assays were performed in duplicate, and MFI values represent the means after blank subtraction. Comparisons of immune complex binding ratios for high-affinity (B) and low-affinity (C) variants of Fcγ3a and Fcγ2a. (D) Area scaling analysis (ASA) was applied to results obtained for week 19 serum samples in the ADCC-GTL assay, and the natural killer (NK) cell-to-monocyte ratio was calculated (see Results). Cell surface expression of CD107a was used as a marker for NK cell degranulation in assays performed using gp120-coated target cells (E) or HIV-infected target cells (F). (G) NK cell degranulation assay performed using PBMC from an unvaccinated RM as effector cells. A human HIV-seropositive plasma sample was used as a positive control. In panels B to G, open circles and squares represent animals that received the systemic i.m./i.m. vaccine regimen, and filled circles and squares represent animals that received the mucosal i.n./i.m.+i.n. vaccine regimen. Medians are indicated with horizontal lines, and error bars indicate the interquartile ranges. P values were calculated by Wilcoxon rank sum tests, with correction for multiple comparisons in panels B and C.