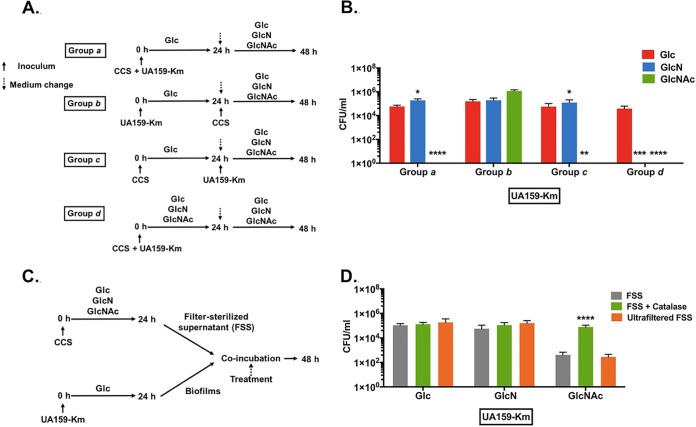
FIG 7.
Amino sugars impact the survival of S. mutans in CCS-derived biofilms. (A and B) To initiate a biofilm, UA159-Km and cell-containing saliva (CCS) were used simultaneously (groups a and d) or 24 h apart (groups b and c) to inoculate BM supplemented with 2 mM sucrose and 18 mM various other carbohydrates. After 24 h of incubation, the biofilms were washed and resupplied with fresh medium and additional bacteria as specified (see Materials and Methods for details). (B) At the end of 2-day incubations, biofilms were processed to quantify the number of CFU of UA159-Km. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences compared to cultures prepared with Glc. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. (C and D) A UA159-Km biofilm was treated for 24 h with a filter-sterilized supernate (FSS) derived from biofilm cultures of CCS that were formed aerobically under different carbohydrate conditions, followed by CFU quantification of UA159-Km (D). The FSS was treated with catalase, passed through an ultrafiltration device (MWCO, 10 kDa), or left untreated. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences compared to untreated FSS. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.