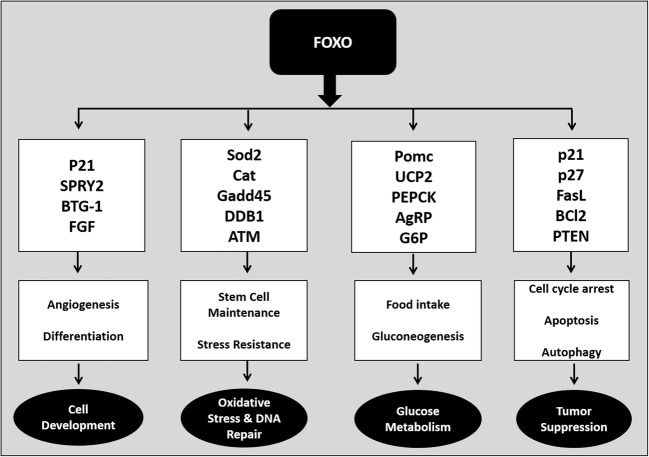
Fig. 4.
Biological role of FOXO family members, target gene activation and cellular functions. Various signaling pathways are involved in phosphorylation and activation/inactivation of FOXO. Once FOXO is stimulated it translocates to the nucleus which leads to the regulation of various downstream genes related to multiple cellular functions such as cell development, cell differentiation, survival, glucose metabolism, oxidative stress and tumor suppression. Note that this figure does not include all FOXO target genes. p21, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A; SPRY2, sprout homolog 2, BTG-1, B-cell translocation gene 1; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; SOD2, superoxide dismustase 2; CAT, catalase; Gadd45, growth arrest and DNA damage inducible protein 45, DDB1, DNA damage-binding protein 1, ATM, ATM serine/threonine kinase, POMC, pro-opiomelanocortin, UCP2, mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2; PEPCK, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; G6P, glucose-6-phosphatase; p27, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B; FasL, Fas ligand; Bcl2, B-cell lymphoma 2 protein; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog