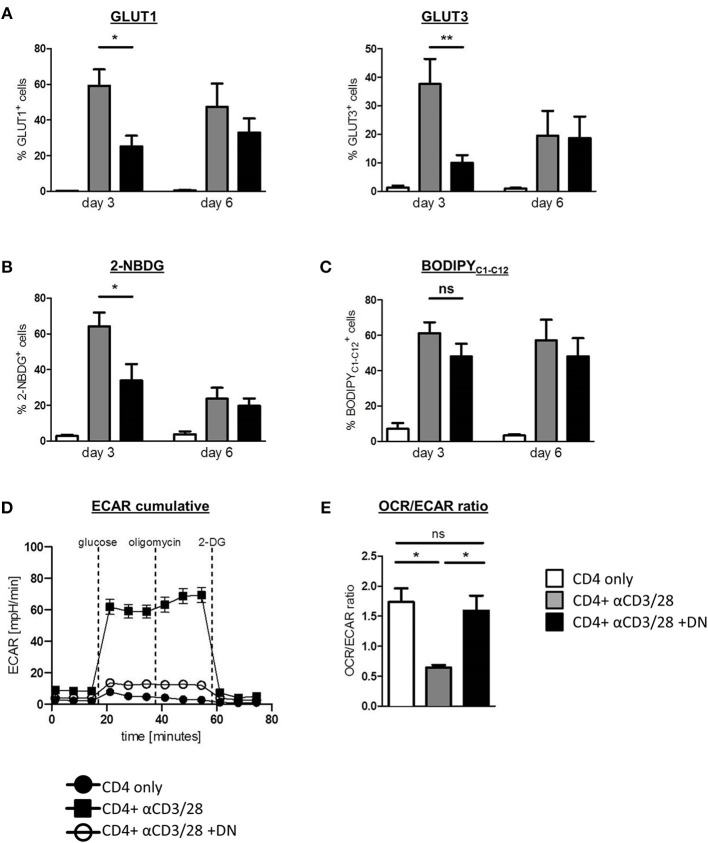
Figure 2.
DN T-cells impair metabolic reprogramming of CD4 T-cells. Freshly isolated CD4 T-cells were incubated with anti-CD3/CD28 coated beads in absence (gray) or presence (black) of DN T-cells, unstimulated CD4 T-cells served as negative control (white). Cells were analyzed by flow cytometry after 3 and 6 days. (A) Expression of GLUT1 and GLUT3 in CD4 T-cells was determined by flow cytometry after 3 and 6 days. (B) Uptake of the glucose analog 2-NBDG and (C) the fatty acid BodipyC1−C12 in CD4 T-cells was measured as described in Materials and Methods. Data of at least seven independent experiments +/- SEM are shown. (D) On day 3 of co-culture CD4 T-cells were re-isolated by magnetic sorting and ECAR was measured in CD4 T-cells, using an XFe96 flux analyzer. (E) The OCR/ECAR ratio indicative for the energetic balance between OXPHOS and aerobic glycolysis was calculated for unstimulated CD4 T-cells and for activated CD4 T-cells in presence or absence of DN T-cells (n = 4). ns, not significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.