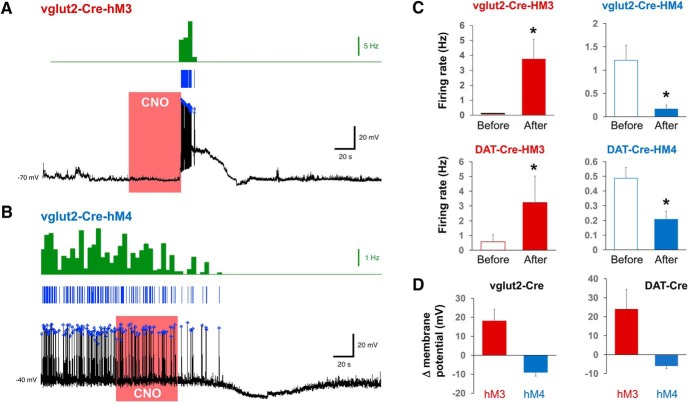
Figure 3.
Functional characterization of hM3 and hM4 DREADDs in vlPAG/dorsal raphe neurons of vGglut2-Cre and DAT-cre mice. A, Whole-cell current-clamp recording from an hM3Dq-expressing vlPAG neuron. Brief bath application of 10 µM CNO (red box) caused a transient depolarization and robust action potential firing in both vGlut2 and DAT neurons. Blue lines represent individual spike events. These were then aggregated into 5-s bins and the frequency plotted as shown in the green histogram. B, Voltage trace showing that bath perfusion with 10 µM CNO caused prolonged membrane hyperpolarization and silencing of both vGlut and DAT vlPAG/dorsal raphe neurons. C, Quantification of the CNO effects on neuron firing rate in grouped vGlut2 and DAT neurons (n = 4). D, Quantification of the CNO effects on membrane potential (all values are mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05).