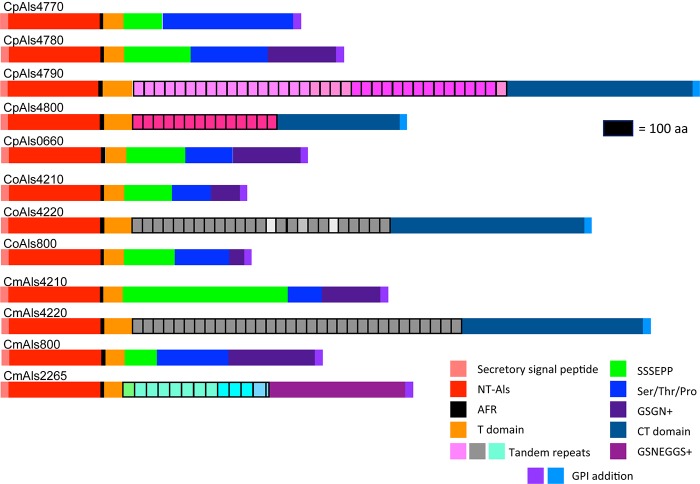
FIGURE 2.
Schematic of proteins predicted from the ALS genes of the C. parapsilosis species complex. Each predicted protein had a secretory signal peptide, a classical NT-Als domain with eight conserved Cys residues to direct folding, an amyloid-forming region (AFR; Garcia et al., 2011), a Thr-rich sequence (T domain), a C-terminal domain rich in Ser/Thr, and a signal for addition of a GPI anchor that directs the mature protein to a final localization linked to β-1,6-glucan in the fungal cell wall (Lu et al., 1994). Only 5 of the 12 proteins included a central domain of tandemly repeated sequences like those found in C. albicans Als proteins (Hoyer et al., 2008). Different colors of the repeated units indicated differences in consensus sequence; shading within the same protein indicated repeat units that varied in the number of amino acids. The other proteins had regions of short, imperfect repeated sequences such as Ser-Ser-Ser-Glu-Pro-Pro (SSSEPP) and/or Gly-Ser-Gly-Asn (GSGN). CmAls2265 had the NT-Als domain attached to tandemly repeated sequences from the Iff/Hyr family (Bates et al., 2007; Boisramé et al., 2011) and a C-terminal region more-characteristic of Iff/Hyr proteins than C. albicans Als proteins.