FIGURE 8.
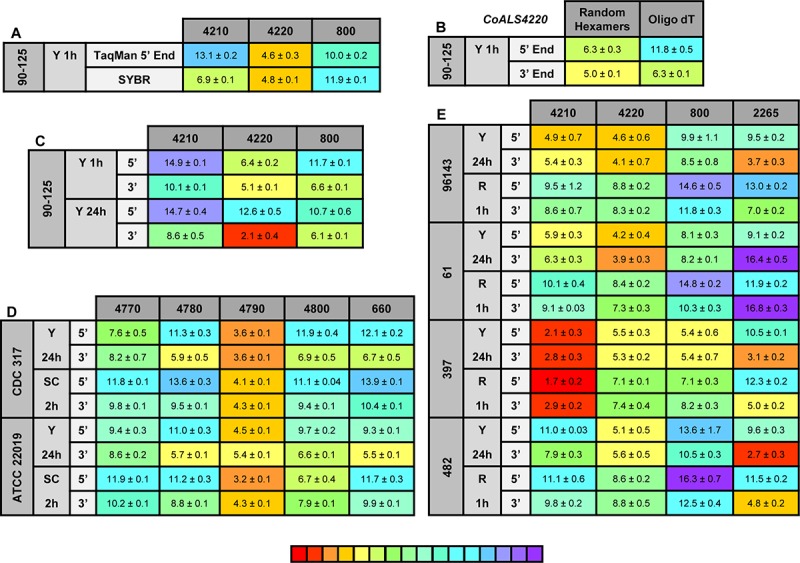
Relative gene expression measured by TaqMan assays. (A) C. orthopsilosis strain 90-125 was grown in YPD for 1 h. RNA preparations from these cells were assayed by TaqMan or the SYBR Green method of Lombardi et al. (2019). Mean (± standard error of the mean) Ct values were reported. Results were shaded to indicate the intensity of relative gene expression. The color key at the bottom of the diagram was shaded from red (high relative gene expression) to purple (low relative gene expression) to facilitate comparison between results. CoALS4220 was expressed more highly than either of the other genes in the growth conditions tested. The SYBR Green method suggested a higher relative expression level for CoALS4210 than did the TaqMan assay. (B) CoALS4220 was used as a model gene to test the effect of cDNA synthesis priming method and TaqMan assay location on estimates of relative gene expression. Placement of the TaqMan assay at the 3′ end of the gene produced higher expression estimates than placement at the 5′ end of the gene. Priming with random hexamers produced a higher gene expression estimate than oligo dT priming. (C) Themes illustrated in (A,B) carried forward to a more-extensive analysis of C. orthopsilosis ALS gene expression. Strain 90-125 was grown for 1 h and 24 h in YPD medium. CoALS4220 was more-highly expressed than the other genes. Estimates of relative gene expression were higher for TaqMan assays at the 3′ end of the gene than at the 5′ end of the gene. (D) Relative expression of C. parapsilosis ALS genes in two strains (CDC317, ATCC 22019) grown in two different conditions (YPD for 24 h; SC with fetal bovine serum for 2 h). CpALS4790 was more-highly expressed than the other genes, even CpALS4800 which was proposed to arise from duplication of CpALS4790. (E) Relative expression of C. metapsilosis ALS genes in four strains (ATCC 96143, 61, 397, 482) in two different growth conditions (YPD for 24 h; RPMI 1640 for 1 h). Considerable strain variation was observed with genes that were relatively quiet in one isolate (e.g., CmALS4210 in strain 482) but extremely highly expressed in another (strain 397). In many instances, gene expression estimates from the 5′ end and 3′ end TaqMan assays provided similar results, although several notable exceptions were present. The apparent lack of CmALS2265 expression in strain 61 (as measured with the 3′ end assay) prompted examination of the gene sequence at the site of the TaqMan assay (Figure 6E). Sequence variation between the TaqMan assay and gene sequence in this region explained the falsely low estimate.
