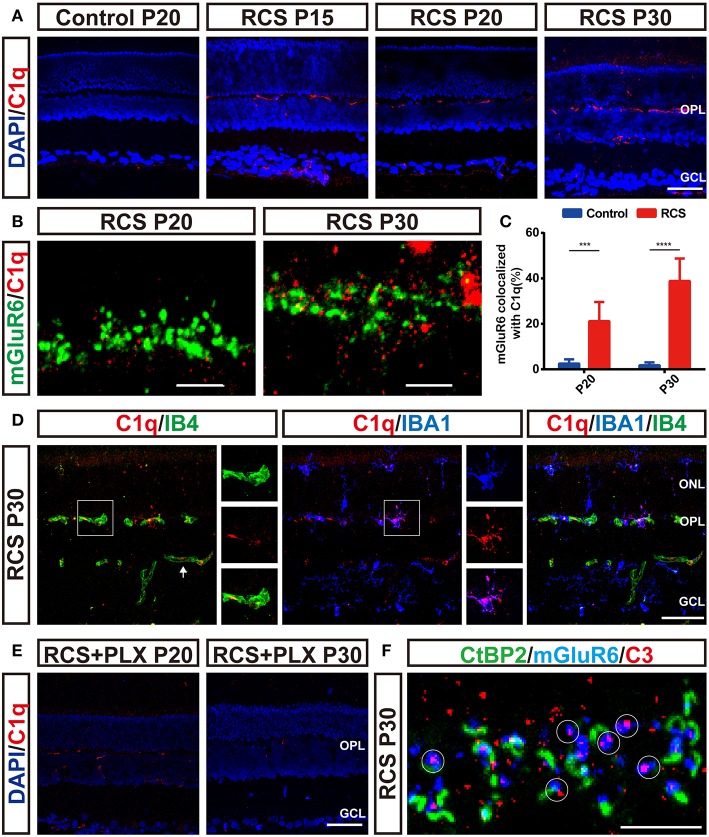
Figure 8.
Microglia-induced C1q upregulation and deposition onto postsynaptic elements precede synapse loss in the OPL during retinal degeneration in RCS rats. (A) Immunostaining for C1q (red) in the retinas revealed region-specific (OPL) upregulation of C1q (red) in RCS rats. (B,C) Confocal images showing an increase in the colocalization of C1q (red) and mGluR6 (green) in RCS rats compared with controls (N = 6 eyes from different rats, n = 6–10 images from each eye). (D) Labeling of the retinal vasculature using isolectin-B4 (IB4) and microglia using IBA1 revealed that C1q in the OPL was mainly derived from the blood circulation and microglia in the P30 RCS rats. White arrows indicated that C1q came from the vasculature in the inner retina. (E) Elimination of microglia with the PLX3397 treatment decreased C1q immunoreactivity in the retinas of RCS rats. (F) Representative confocal image showing the colocalization of C3 (red) and mGluR6 (blue) but a lack of colocalization with CtBP2 (green) in the retinas of P30 RCS rats. White circles indicate C3 deposition onto unpaired mGluR6. ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer. Scale bar, 50 μm (A,D,E), 5 μm (B,F). Bars represent means; error bars represent SD. ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 using two-way ANOVA (C).