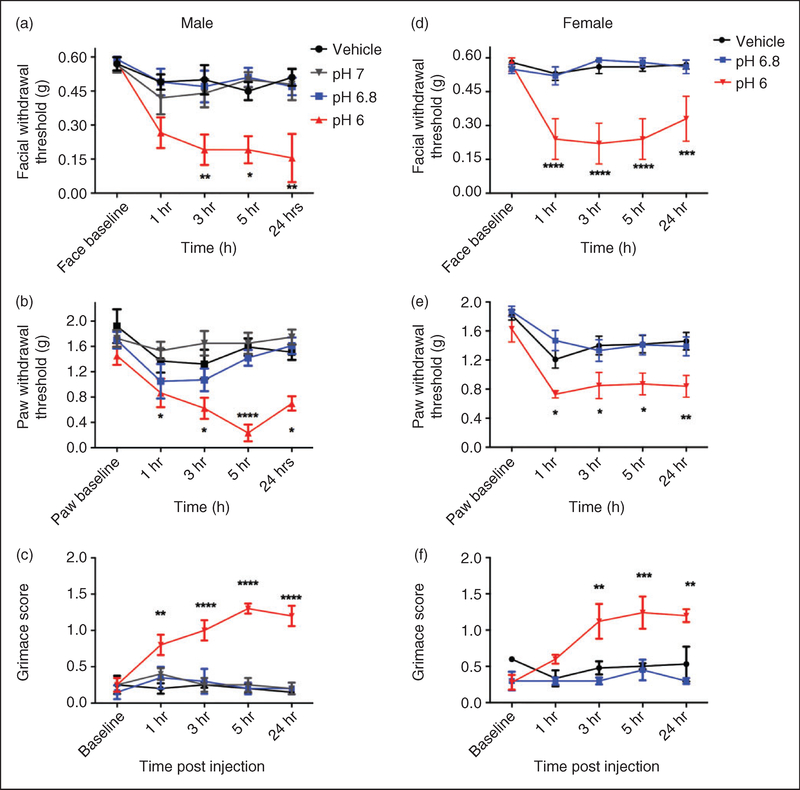
Figure 2.
Non-invasive dural application of pH 6.0 produces headache-related behavior in male and female mice. Dural application of low pH (pH 6) produces cutaneous hypersensitivity in both male ((a), (b)) and female mice ((d), (e)). Withdrawal thresholds to tactile stimuli applied to the face (a) and hindpaws of male mice (b) were measured in animals prior to and following dural application of pH 6.0 (1–5 hr; n = 13, 24 hr; n = 7), pH 6.8 (n = 8) pH 7.0 (n = 7) or vehicle (pH 7.4; n = 8). In males, only administration of pH 6.0 produced significant facial (a) and hindpaw (b) responses. Similarly, female withdrawal thresholds to tactile stimuli applied to the face (d) and hindpaws (e) were measured in animals prior to and following dural application of pH 6.0 (n = 11), pH 6.8 (n = 8) or vehicle (pH 7.4, n = 16). In females, dural administration of pH 6 produced significant facial (d) and hindpaw (e) responses. Grimace behaviors were significant in males (n = 5, (c)) and in females (n = 5, (f)). Two-factor analysis of variance (ANOVA) indicated a significant effect of both treatment and time of both the face and hindpaws. Significant differences among means for each group were determined by analysis of variance followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. Males (a) facial: Time F (4, 154) = 6.631, p < 0.0001, treatment F (3, 154) = 18.12, p < 0.0001; (b) hindpaw: Time F (4, 154) = 5.7, p < 0.0001, treatment F (3, 154) = 22.75, p< 0.0001; (c) grimace: Time F (4,80) = 3.976, p= 0.00054, treatment F (3, 80) = 51.78, p < 0.0001. Females (d) facial: Time F (4, 160) = 4.64, p= 0.0014, treatment F (2, 160) = 54, p < 0.0001; (e) hindpaw: Time F (4, 160) = 11.26, p < 0.0001, treatment F (2, 160) = 22.64, p < 0.0001; (f) grimace: F (4, 60) = 4.332, p= 0.0038, treatment F (2, 60) = 24.41, p < 0.0001