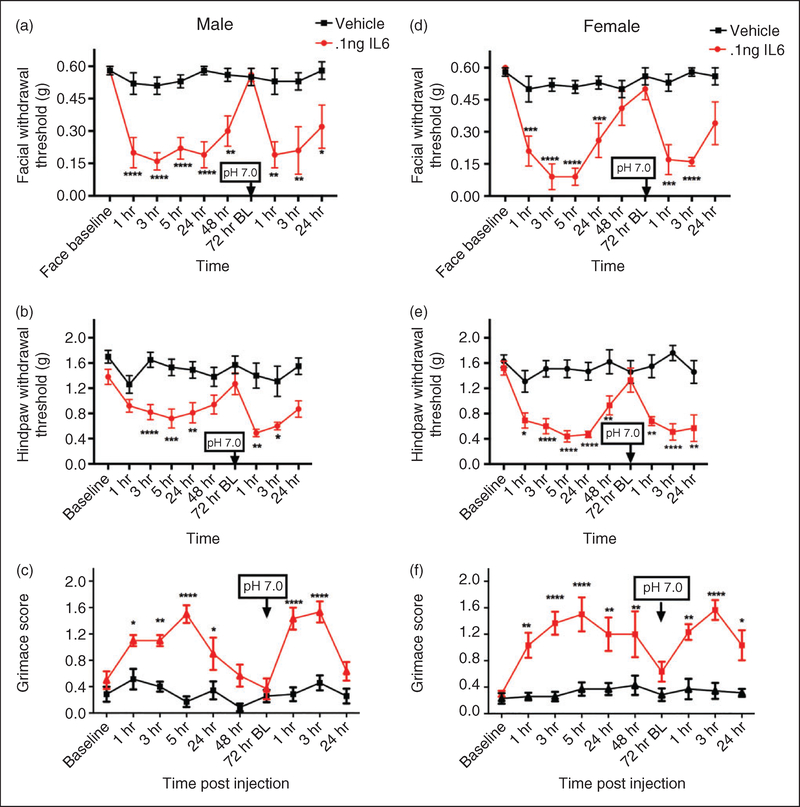
Figure 3.
Non-invasive dural application of IL-6 produces headache-related behavior in both male and female mice. Dural application of IL-6 (0.1 ng) produces cutaneous hypersensitivity in both male ((a), (b)) and female mice ((d), (e)). Males treated with IL-6 (1–48 hr; n = 13, 72 hr BL and later; n = 7), showed significant facial (a) and hindpaw (b) responses and also significant responses to subsequent dural pH 7.0. Similarly, females treated with IL-6/dural pH 7.0 (1–48 hr; n = 12, 72 hr BL and later; n = 7) had significant facial (d), and hindpaw (e) responses and also significant responses to subsequent dural pH 7.0. Grimace behaviors were significant in males (n = 6, all timepoints; (c) and in females (n = 7, (e)). Significant differences among means for each group were determined with one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. Males facial: Time F (9, 177) = 4.768, p < 0.0001, treatment F (1, 177) = 106.5, p < 0.0001; hindpaw: Time F (9, 166) = 3.135, p= 0.0016, treatment F (1, 166) = 82.65, p < 0.0001); grimace: Time F (9, 110) = 7.305, p < 0.0001, treatment F (1, 110) = 127.4, p < 0.0001. Females facial: Time F (9, 151) = 6.818, p < 0.0001, treatment F (1, 151) = 120.7, p < 0.0001; hindpaw: Time F (9, 151) = 3.758, p < 0.0001, treatment F (1, 151) = 130.4, p < 0.0001); grimace: Time F (9, 110) = 3.578, p= 0.0004, treatment F (1, 110) = 125.8, p < 0.0001.