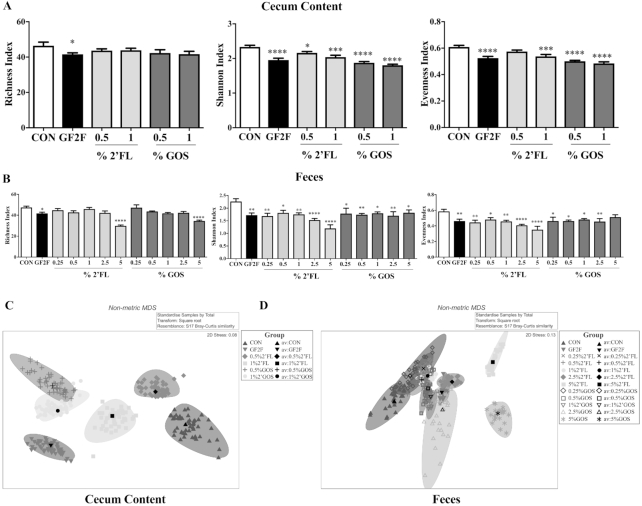
FIGURE 6.
Impact of GF2F diet on α-diversity indices in the (A) cecal content (CC) and (B) feces, and β-diversity overall microbial community structure at the taxonomic level of genus in CC (C) and feces (D) of vaccinated mice. Diversity indices (Shannon, richness and evenness) are depicted at the taxonomic level of genus. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 8–9/group. Significantly different from CON: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. One-way analysis of variance test for parametric data and Bonferroni's post-hoc test were used in panel A. The Kruskal-Wallis test for nonparametric data and Dunn's post-hoc test were used in panel B. Nonmetric multidimensional scaling of bootstrap averages for the CON and treatment groups in CC (C) and feces (D). Colored ovals represent the 95% region estimates for the mean communities in each treatment group. Black symbols represent the group means of the repeated bootstrap averages. ANOSIM is used to assess statistical significance of divergent microbial community structure (Supplemental Table 2). ANOSIM, analysis of similarity; CC, cecum content; CON, control; GF2F, scGOS/lcFOS/2′FL (2′FL, 2′-fucosyllactose; FOS, fructo-oligosaccharides; GOS, galacto-oligosaccharides; lc, long chain; sc, short chain).