Figure 3.
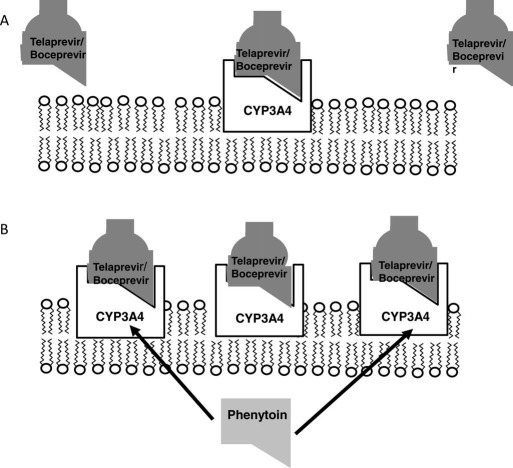
Mechanism of CYP3A4 induction and reduced bioavailability of telaprevir/boceprevir. (A) Telaprevir and boceprevir are metabolized in hepatocytes, which have a constitutive but inducible level of CYP3A4 enzyme activity. (B) The administration of select drugs such as phenytoin and efavirenz can lead to the induction of additional CYP3A4 gene expression via the activation of intracellular nuclear receptors. This induction leads to greater amounts of CYP3A4 protein expression in the endoplasmic reticulum, which can lead to enhanced metabolism and the elimination of telaprevir or boceprevir. The net effect of CYP3A4 induction includes a potential reduction in the local and systemic bioavailability of the DAAs and a higher rate of treatment failure and drug resistance in HCV genotype 1 patients.
