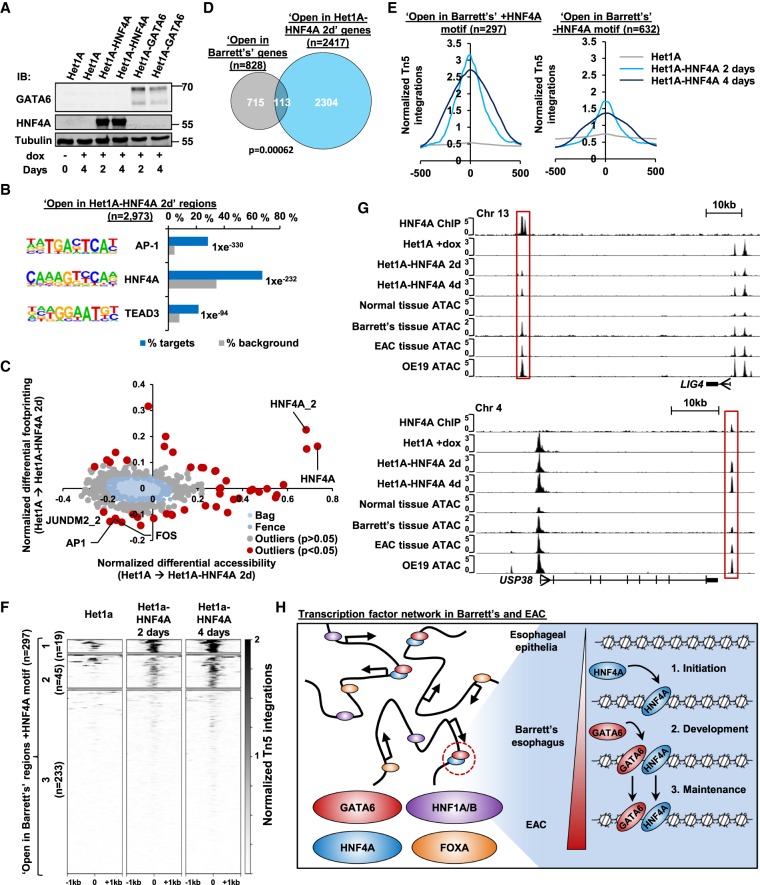
Figure 5.
HNF4A demonstrates pioneer factor function. (A) Immunoblot analysis of HNF4A, GATA6, and tubulin alpha in Het1A, Het1A-HNF4A, and Het1A-GATA6 cells. The addition of doxycycline for 2 or 4 days is indicated (+). (B) The top three DNA motifs derived from de novo motif discovery of differentially accessible regions in Het1A-HNF4A cells after 2 d of induction and their associated transcription factors. The frequency of motif occurrence is shown, and the motifs are sorted by P-value. (C) Scatter bag plot of differential chromatin accessibility (x-axis) and footprinting (y-axis) depth around human transcription factor binding motifs in Het1A and Het1A-HNF4A cells. Significant outliers (P < 0.05) are represented in red. Motifs with enrichment in “open in Het1A-HNF4A” regions are labeled. (D) Overlap of genes annotated to “open in Barrett's” and “open in Het1A-HNF4A 2d” regions. P-value was calculated using the hypergeometric test. (E) Tag density plots of ATAC-seq signal from Het1A and Het1A-HNF4A cells (2 and 4 d doxycycline induction) around differentially open regions in Barrett's tissue with (left) or without (right) a HNF4A consensus binding motif. (F) Heatmap of ATAC-seq signal from Het1A and Het1A-HNF4A cells (2 and 4 d doxycycline induction) at “open in Barrett's” regions with a HNF4A motif. Regions were subjected to k-means hierarchical clustering (k = 3). (G) UCSC Genome Browser tracks of two example loci at LIG4 and USP38, with regions boxed that show increased accessibility with HNF4A overexpression. (H) Model of the transcription factor network in Barrett's and EAC. HNF4A is able to promote chromatin opening in normal esophageal cells at a subset of Barrett's-specific regions. In Barrett's, a transcription factor network, including HNF4A and GATA6 are coexpressed, and these two transcription factors co-occupy a large number of genomic regions. This regulome persists in the context of the chromatin landscape of EAC cells.