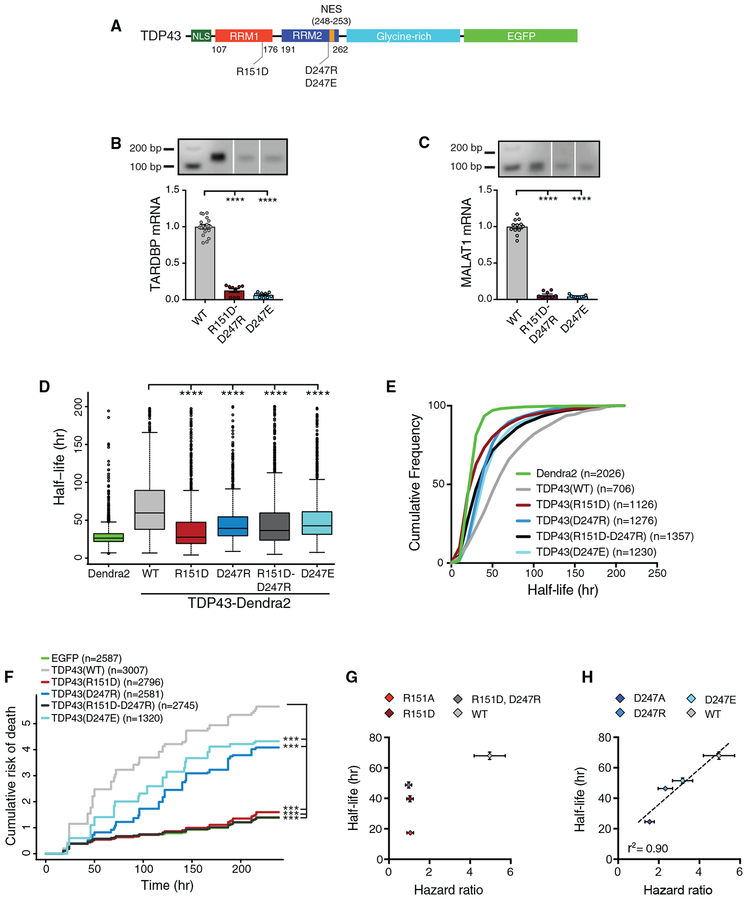
Figure 5. Arg151 Mutations Interrupt the Proportional Relation between TDP43 Stability and Toxicity.
(A) Illustration of TDP43 variants tested in (B)–(F).
(B and C) RNA IP of TARDBP (B) and MALAT1 (C) transcripts in HEK293T cells expressing EGFP-tagged TDP43 variants.
(D) Significant decreases in protein half-life were observed for all TDP43 variants compared to TDP43(WT), as determined by OPL.
(E) Cumulative frequency plot of data shown in (D).
(F) By automated neuronal survival analysis, TDP43(WT)-EGFP was significantly toxic compared to EGFP (HR = 4.42, p < 2 × 10−16). All TDP43 variants were less toxic than TDP43(WT)-EGFP (R151D, HR = 0.23; D247R, HR = 0.48; R151D-D247R, HR = 0.21; D247E, HR = 0.6; p < 2 × 10−16 for all comparisons). Cells expressing either TDP43(D247R)-EGFP or TDP43(D247E)-EGFP demonstrated a significantly elevated risk of death compared to those expressing EGFP (HR = 2.2 and 2.76, respectively; p < 2 × 10−16 for both comparisons).
(G and H) While no relation was observed between half-life and toxicity for R151 variants (G), D247A variants displayed a linear relation between half-life and toxicity (H).
For (B) and (C), data were pooled from 3 independent experiments, ****p < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s test. For (D), data were pooled from 4 replicates, ****p < 0.05, 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test. For (F), data represent 3 replicates, ***p < 2 × 10−16, Cox proportional hazards. n, number of neurons. For (G) and(H), error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. In (H), r2 calculated by nonlinear least-squares regression.