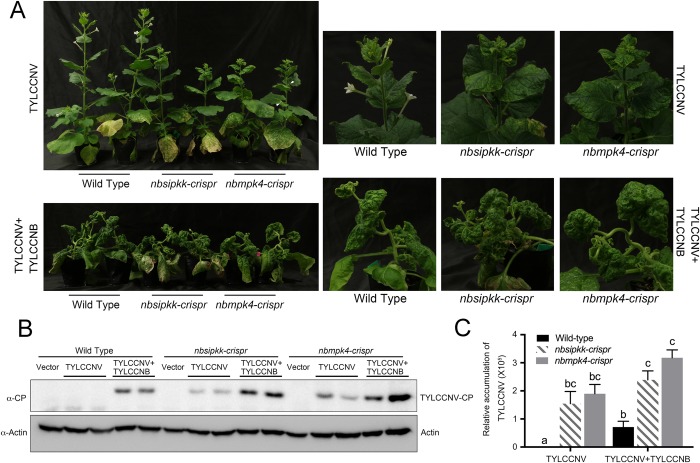
Fig 5. MKK2 and MPK4 participate in basal defense against virus.
(A) nbsipkk-crispr plants and nbmpk4-crispr plants displayed severe growth defect with TYLCCNV and TYLCCNV/TYLCCNB infection. Eight-leaf-period wild-type, nbsipkk-crispr and nbmpk4-crispr N. benthamiana leaves were infiltrated with A. tumefaciens harboring TYLCCNV or TYLCCNV/TYLCCNB infectious clone. Plant phenotype was monitored 30 days after inoculation. (B) Western blot analysis of virus titers in wild type, nbsipkk-crispr or nbmpk4-crispr plants. Virus amount was detected by the immunoblot assay with a TYLCCNV-CP antibody. (C) Relative accumulation levels of TYLCCNV in agroinfiltrated wild type, nbsipkk-crispr or nbmpk4-crispr plants. Viral accumulation was determined by qPCR at 30 dpi. The values represent viral DNA accumulation relative to levels in TYLCCNV infected wild type plants. The data are shown as means and SEM of three biological replicates. Different letters indicate significant differences among samples (p<0.05, Student’s t test).