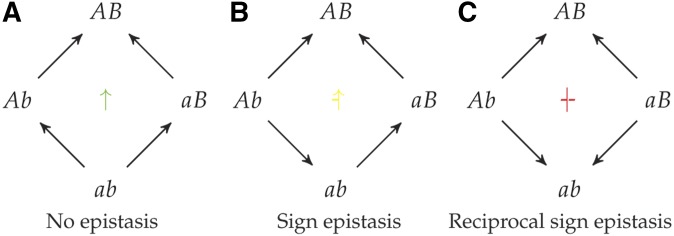
Figure 1.
Three different kinds of epistasis possible in fitness graphs: (a) no epistasis, (b) sign epistasis, and (c) reciprocal sign epistasis. Arrows are directed from lower fitness genotypes toward mutationally adjacent higher fitness genotypes. Genes and are labeled such that fitness . In the center of each graph is a marker for the type of epistasis, the marker’s various rotations and reflections cover the cases where does not have the highest fitness. For this more exhaustive classification and discussion see SA Figure A.1 and SA A.1.