Table A1. Summary of main results.
| Landscape type | Max allowed epistasis type | Hardness of reaching local optima | Proved in... |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smooth | magnitude () | Easy for all strong-selection weak-mutation (SSWM) dynamics | Section B |
| Semismooth | sign (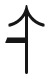 , ,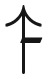 ) ) |
Hard for SSWM with random fitter mutant | Theorems 15, |
| or fittest mutant dynamics | 20, and 24 | ||
| Rugged | reciprocal sign (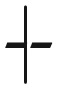 ) ) |
Hard for all SSWM dynamics: initial genotypes with all adaptive paths of exponential length | Corollary 28 |
| Hard for all evolutionary dynamics (if FP ≠ PLS) | Theorem 27 | ||
| Easy for finding approximate local peaks with moderate optimality gap: selection coefficients can drop-off as power law | Theorem 33 | ||
| Hard for approximate local peaks with small optimality gap: | Theorem 35 | ||
| selection coefficient cannot drop-off exponentially | Corollary 36 |
Each landscape type (column 1) is characterized by the most complicated permitted type of epistasis (column 2; see A.1). Based on this, there are families of this landscape type that are easy or hard under progressively more general dynamics (column 3), which is proved in the corresponding part of the appendix (column 4).
