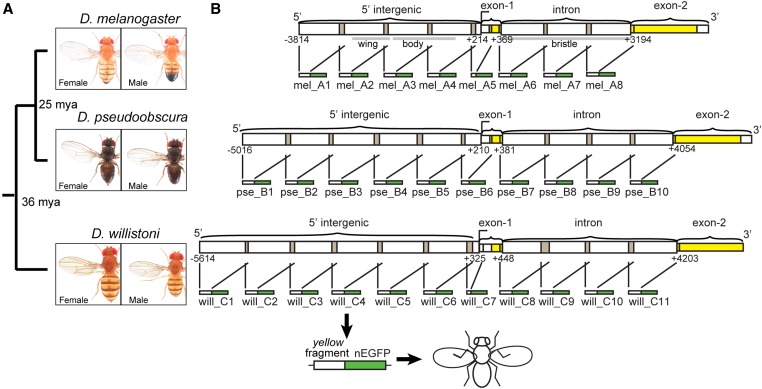
Figure 1.
Fragments of yellow 5′ intergenic and intronic sequences tested for enhancer activity. (A) Divergence times among D. melanogaster, D. pseudoobscura, and D. willistoni are shown, along with images of adult males and females from each species. (B) Schematics show the overlapping fragments from regions of 5′ intergenic and intronic sequence of yellow from each species tested for enhancer activity. Each of these ∼1 kb fragments was cloned upstream of a nuclear Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein (nEGFP) to form a reporter gene, and each reporter gene was inserted into the attP40 landing site on chromosome arm 2L. Gray bars under the D. melanogaster schematic show the borders of previously identified tissue-specific enhancers of yellow driving expression in the wing, body, and bristles (Geyer and Corces 1987; Wittkopp et al. 2002; Kalay and Wittkopp 2010). This schematic was modified from Kalay et al. (2016). Pictures of Drosophila species generously provided by Nicolas Gompel (Ludwig-Maximilians-University of Munich).