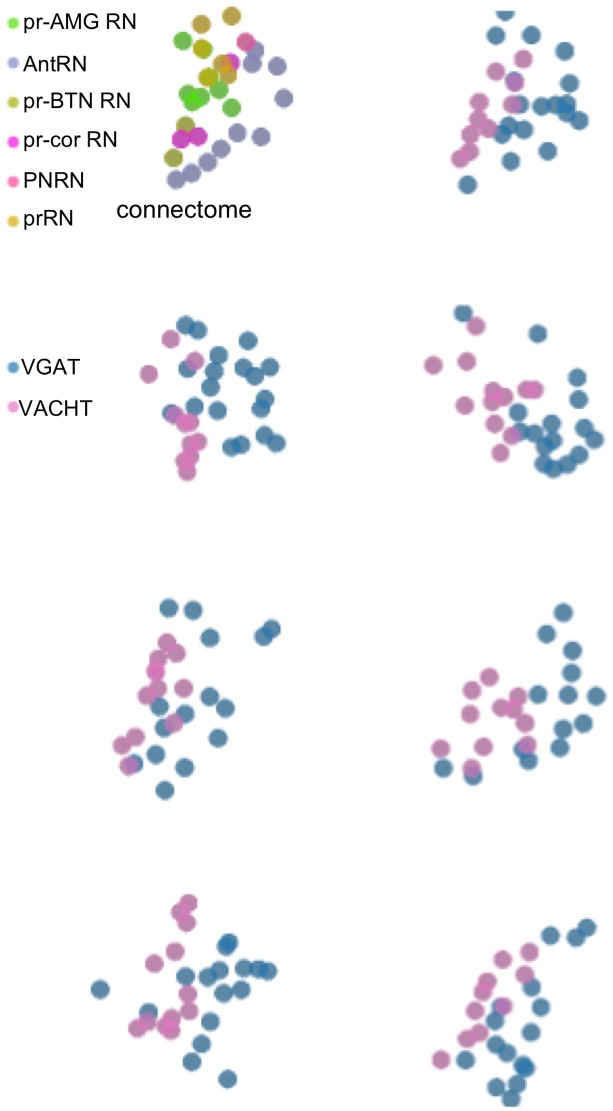
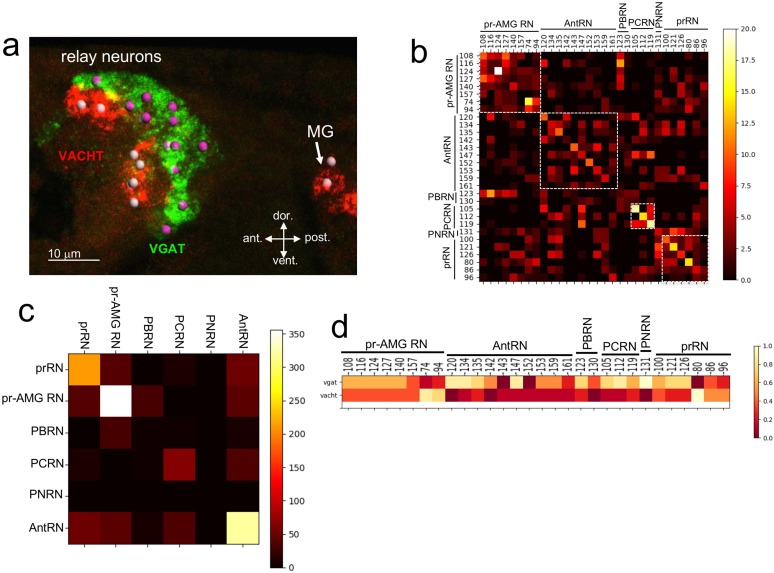
Figure 3. Neurotransmitter use in the relay neurons.
(a) In situ hybridization of VGAT and VACHT to the relay neurons in the brain vesicle. Also visible is the anterior tip of the motor ganglion. Nuclei are shown as spheres. (b) Confusion matrix for relay neuron registration. (c) Confusion matrix for relay neurons grouped by type. (d) Heat map of neurotransmitter predictions from cell registration of relay neurons, with scale showing color by proportion of iterations predicting either VGAT or VACHT. Abbreviations: ant., anterior; post., posterior; dor., dorsal; vent., ventral; MG, motor ganglion; pr-AMG RN, photoreceptor ascending motor ganglion relay neuron; prRN, photoreceptor relay neuron; AntRN, antenna cell relay neuron; PBRN, photoreceptor-bipolar tail neuron relay neuron; PCRN, photoreceptor-coronet relay neuron; PNRN, peripheral relay neuron; VGAT, vesicular GABA transporter; VACHT, vesicular acetylcholine transporter.