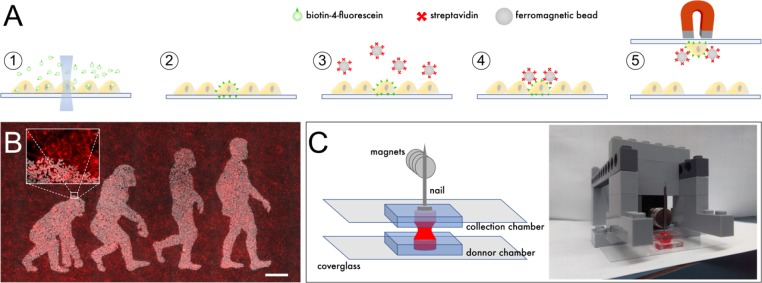
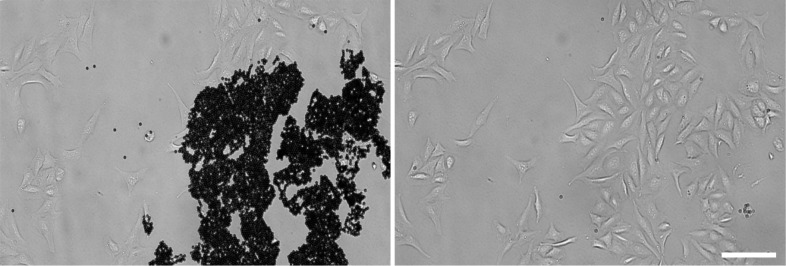
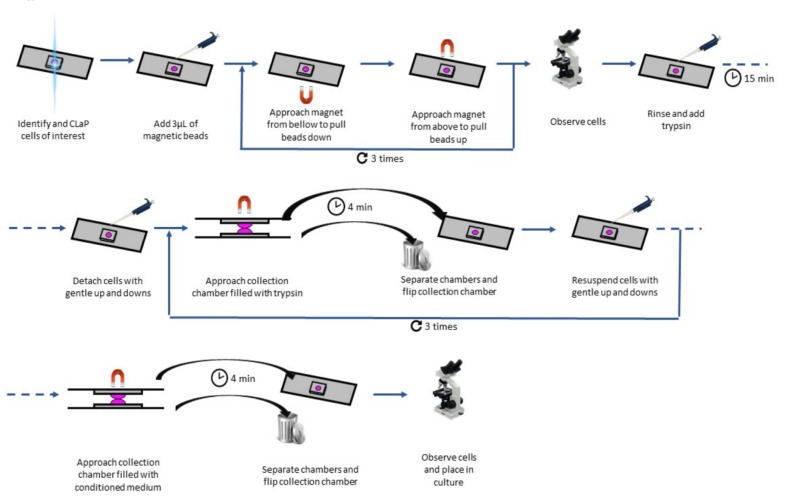
Figure 1. Outline of scMOCa.
(A) Biotin-4-fluorescein is crosslinked to cell membranes with a laser. Biotin-tagged cells are labeled with streptavidin-coated ferromagnetic beads and captured with a magnet. (B) Example of a confluent U2OS cell culture where only cells illuminated with the lasers of a confocal microscope are densely decorated with magnetic particles. Beads appear in white, and all cellular membranes in red, tagged with WGA-Alexa647. Scale bar: 500 µm. (C) Schematic illustrating the simple tools needed to implement the protocol. Two small cell culture chambers cast in silicone and adhered to coverglasses are positioned one on top of the other. Cells in the bottom chamber are attracted to the top collection chamber by a magnetic field. A nail is placed above the collection chamber to guide the field generated by magnets to the donor chamber in which the cell suspension is kept. The collection chamber is held between two Lego bricks, filled with a solution of Trypsin (held in place by surface tension), and then slowly approached 6 mm above the bottom chamber, at which point the two drops merge.