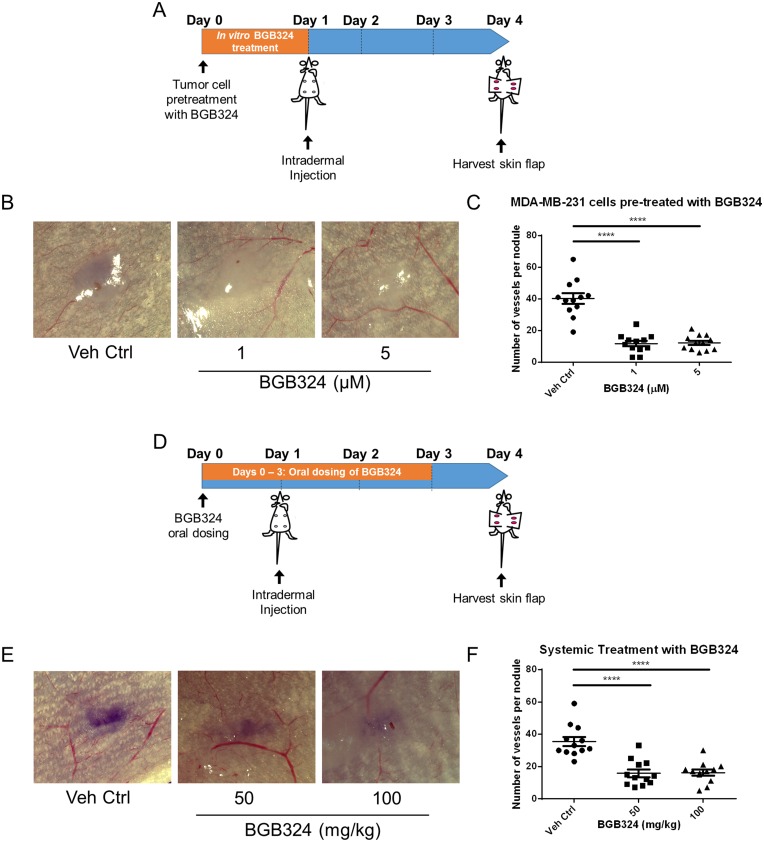
Figure 6. BGB324 impairs in situ angiogenesis.
(A) Scheme of the intradermal assay. MDA-MB-231 cells were pre-treated with BGB324 for 24 h prior to inoculation. Tumor cells were injected intradermally at four sites on the ventral surface of athymic nu/nu mice (105 cells per nodule). (B) Representative images of MDA-MB-231 tumor nodules where tumor cells were pre-treated with BGB324 for 24 h prior to inoculation. (C) The number of vessels recruited per tumor nodule was counted three days later for mice inoculated with pre-treated MDA-MB-231 cells: vehicle control (Veh Ctrl), 1-, or 5- μM BGB324 for 24 h prior to tumor cell inoculation. (D) Scheme of the intradermal assay. Daily oral dosing with BGB324 (50- or 100- mg/kg BGB324) or agent vehicle control began a day before tumor inoculation and continued for 3 days. MDA-MB-231 cells were inoculated intradermally at four sites on the ventral surface of athymic nu/nu mice (105 cells per nodule). (E) Representative images of MDA-MB-231 tumor nodules with systemic BGB324 treatment. (F) The number of vessels recruited per tumor nodule was counted three days later for mice inoculated with MDA-MB-231 cells. Mice received vehicle control (Veh Ctrl), 50-, or 100- mg/kg BGB324 via oral gavage. Results are the mean and standard error values, with twelve nodules per group analyzed. ****p < 0.00001; by one-way ANOVA.